The United Nations
The United Nations fosters global peace, security, and cooperation. Explore its history, impact, and role in shaping international relations and policies.
1.1 – What is The United Nations and Why It Matters?
Discover what the United Nations is, its mission, and why it plays a crucial role in global peace, security, and human rights, shaping a better world for all.
The United Nations (UN) is one of the most influential international organizations, founded in 1945 after the devastation of World War II. Its primary goals include promoting peace, security, and cooperation among nations while addressing global challenges such as poverty, human rights, and climate change.
The U.S. played a pivotal role in the creation of the UN, with leaders like Franklin D. Roosevelt envisioning an organization to prevent future wars. As Roosevelt famously stated, “The structure of world peace cannot be the work of one man, one party, or one nation… It must be a peace which rests on the cooperative effort of the whole world.” This quote reflects the UN’s foundational vision of global cooperation.
Today, the UN continues to be crucial in addressing humanitarian crises and environmental sustainability, with the U.S. actively engaging in these international efforts.

1.2 – Historical Background of The United Nations
Discover the origins of the United Nations, its founding principles, and key historical events that shaped its role in global peace, security, and cooperation.
The historical background of The United Nations is essential for understanding its purpose, structure, and continued relevance in today’s global landscape. The UN was founded in 1945 to prevent another devastating conflict like World War II. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, one of the visionaries behind the UN’s creation, said, “The only thing we have to fear is fear itself.” This sentiment of resilience and hope for a peaceful future was fundamental to the formation of the UN. The original 51 member states, including the U.S., sought to create a platform for resolving disputes without resorting to war.
1.2.1 – How the League of Nations Led to the Creation of the UN
To understand the United Nations, it is important to first examine its predecessor, the League of Nations. Founded after World War I in 1920, the League was the first international organization designed to maintain world peace. However, the League failed due to the lack of involvement from key global powers—most notably, the United States—and its inability to prevent the outbreak of World War II. This failure highlighted the need for a stronger, more unified organization.
1.2.2 – How WWII Led to the Creation of The United Nations
The devastation of World War II made it clear that the world needed a stronger framework for peace. The U.S. played a pivotal role in the discussions that led to the establishment of The United Nations. The 1945 San Francisco Conference, where the UN Charter was drafted, was the culmination of these efforts. Attended by representatives from 50 nations, it resulted in a charter aimed at fostering international cooperation, preventing war, and promoting human rights.
1.2.2.1 – Winston Churchill on the Role of The United Nations in Global Peace
Winston Churchill, another founding voice of the UN, stated, “The United Nations was set up not to get us to heaven, but to save us from hell.” This quote encapsulates the UN’s purpose as a safeguard for humanity during times of crisis.
1.2.3 – What Are the Core Goals of The United Nations?
At its core, The United Nations was established with the following goals
1.2.3.1 – How The United Nations Maintains Global Peace and Security
The UN was designed to provide a platform for dialogue and diplomacy to resolve conflicts without military action.
1.2.3.2 – How The United Nations Promotes Global Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted in 1948, remains one of the UN’s greatest achievements, setting a global standard for basic human rights.
1.2.3.3 – How the United Nations Fosters Social and Economic Growth
Through various programs and specialized agencies like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), the UN works to address global issues such as poverty, health crises, and education.
1.2.3.4 – How The United Nations Upholds International Law
The UN plays a crucial role in establishing and enforcing international laws, particularly through the International Court of Justice.
1.2.4 – The Role of the U.S. in UN Security Council Decisions
The U.S. has had a significant influence on the United Nations since its inception. As one of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council, the U.S. wields substantial power in shaping international policies, particularly regarding peacekeeping operations, sanctions, and humanitarian interventions. This involvement highlights the interdependent relationship between the U.S. and the UN, with the U.S. benefiting from the global stability the organization promotes.
1.2.5 – How the Cold War Affected UN Peacekeeping Missions
The Cold War (1947-1991) presented one of the greatest challenges to The United Nations. The ideological conflict between the U.S. and the Soviet Union often paralyzed decision-making within the UN Security Council, with both superpowers using their veto power to block each other’s initiatives. Despite these tensions, the UN played a key role in peacekeeping missions and humanitarian efforts during this period.
1.2.6 – Historic UN Milestones Shaping Global Diplomacy
Over the decades, the United Nations has achieved significant milestones in global diplomacy
1.2.6.1 – Universal Declaration of Human Rights by The United Nations (1948)
A groundbreaking document that established a common standard for human rights across the world.
1.2.6.2 – How the UN Resolved the Suez Crisis in 1956 (1956)
The UN intervened to resolve the conflict between Egypt, Israel, France, and the UK, marking one of its early successful peacekeeping missions.
1.2.6.3 – How the UN’s Millennium Development Goals Addressed Global Poverty (2000)
A set of eight international development goals that were adopted by all 189 UN member states to address poverty, education, and health issues by 2015.
1.2.6.4 – How the United Nations Facilitated the Paris Agreement (2015)
A landmark agreement within the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) aimed at limiting global warming and addressing climate change.
1.2.7 – How the United Nations Has Shaped Modern International Relations
The legacy of The United Nations is one of perseverance and hope. While the organization has faced numerous challenges—ranging from geopolitical conflicts to criticisms of bureaucracy—it remains a crucial player in addressing the world’s most pressing issues. The UN’s role continues to be relevant as nations seek sustainable peace and security.
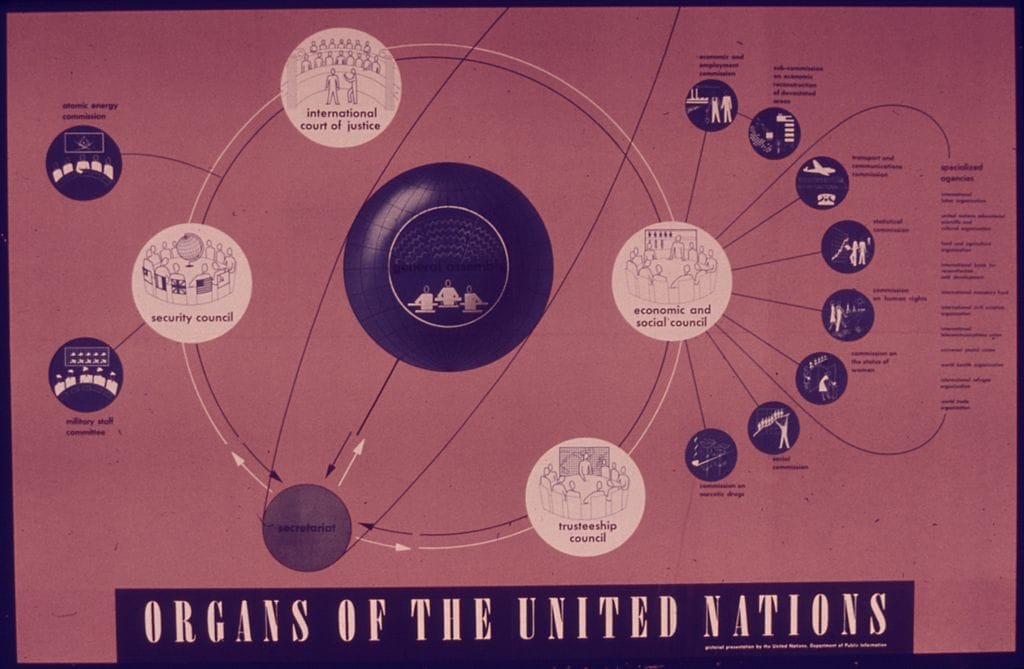
Illustration depicting the organs of the United Nations, emphasizing key components such as the Security Council, General Assembly, and International Court of Justice.
1.3 – Mission of the United Nations in fostering international cooperation
Discover how the United Nations fosters international cooperation, promotes peace, and addresses global challenges to create a more stable and just world.
The United Nations (UN), established in 1945, aims to prevent future conflicts and bring nations together to pursue global peace. Over the years, the UN’s mission has expanded to include a range of objectives such as fostering development, upholding human rights, and addressing climate change.
1.3.1 – UN efforts in maintaining international peace and security
The United Nations’ main objective is to uphold global peace and security. Among its six key bodies, the UN Security Council is responsible for managing peacekeeping efforts, imposing sanctions, and authorizing military interventions when required. Since its inception, the UN has been actively involved in various conflicts, deploying peacekeeping troops—commonly known as “Blue Helmets”—to help stabilize conflict zones, enforce ceasefires, and safeguard civilians.
1.3.2 – How the United Nations defends human rights
A key goal of the UN is the promotion and protection of human rights, driven by the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) adopted in 1948. The UN has developed several bodies, such as the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) and the Human Rights Council, to monitor and address abuses worldwide, from genocide to political repression.
1.3.3 – How the UN fosters economic and social progress
The UN plays a vital role in fostering global economic and social development through agencies like the UN Development Programme (UNDP), World Health Organization (WHO), and UNICEF. In 2015, the UN introduced the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a set of 17 global goals aimed at creating a more sustainable future by 2030. These goals cover issues such as clean water, affordable energy, and climate protection.
1.3.4 – International Court of Justice and United Nations law
The UN also contributes significantly to the development and enforcement of international law. Through the International Court of Justice (ICJ), the UN settles legal disputes and provides advisory opinions. The establishment of the International Criminal Court (ICC) in 2002 was a significant milestone, aimed at prosecuting individuals responsible for war crimes and crimes against humanity.
1.3.5 – How the United Nations Leads Global Environmental Initiatives
The UN has placed increasing emphasis on climate change and environmental sustainability. Through initiatives like the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the 2015 Paris Agreement, the UN leads global efforts to limit global warming to below 2°C and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
1.3.6 – The United Nations and global humanitarian aid initiatives
The UN plays a crucial role in providing humanitarian aid during emergencies. Agencies like the World Food Programme (WFP) and UNICEF provide essential support during natural disasters, conflicts, and health crises. For example, the UN-coordinated global health responses during the COVID-19 pandemic through the World Health Organization (WHO).
1.3.7 – UN’s role in uniting countries for global challenges
The UN serves as a platform for international cooperation, facilitating diplomatic negotiations and global summits. Through its work, the UN strives to unite nations in addressing global challenges, emphasizing that its role is not just idealistic, but a pragmatic necessity.
1.3.8 – The United Nations mission in global peace, rights, and development
The United Nations’ mission encompasses vital goals such as promoting global peace, human rights, sustainable development, and international cooperation. Its efforts in peacekeeping, human rights protection, climate action, and humanitarian assistance continue to shape global diplomacy and influence international policies.
1.4 – Understanding the structure of the United Nations and its key bodies
Discover how the United Nations operates, its key bodies, and their roles in global governance. Gain insights into its structure and impact on international affairs.
Understanding the Structure and Key Bodies of the UN is essential for those interested in global governance. The United Nations (UN) plays a crucial role in international relations, and its complex framework impacts issues like peace, human rights, health, and security.
The UN consists of various bodies, each with specific functions and responsibilities. These structures help the organization fulfill its mission and address global challenges. Understanding them can also show how individuals can engage with and contribute to global initiatives.
1.4.1 – How the UN General Assembly addresses international issues
The UN General Assembly (GA) is the most representative body of the United Nations, comprising all 193 member states, each with one vote. The GA serves as a forum where member nations discuss and collaborate on international issues. The Assembly meets annually in September, with world leaders presenting their views on global matters.
The GA debates global concerns, adopts resolutions, and approves the UN budget. While its resolutions are non-binding, they carry moral and political significance. The General Assembly provides a critical platform for countries to voice their positions on issues like climate change and disarmament.
1.4.1.1 – Eleanor Roosevelt’s vision of human rights and the UN General Assembly’s impact
Eleanor Roosevelt once said, “Where, after all, do universal human rights begin? In small places, close to home.” This highlights the importance of the GA in addressing both local and global issues.
1.4.2 – How the United Nations Security Council maintains global peace
The UN Security Council (UNSC) is the most powerful body within the UN system, tasked with maintaining international peace and security. It consists of 15 members, including five permanent members—China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States—along with ten elected members. The UNSC can impose sanctions, authorize military action, and establish peacekeeping operations.
The concept of collective security underpins the UNSC’s operations. When a threat to peace is identified, the Council convenes to decide on actions, reflecting the consensus of the international community. UNSC decisions involving military interventions or sanctions are binding on all member states.
The Security Council’s structure and operations have sparked debate, especially concerning the power dynamics among permanent members.
1.4.2.1 – Kofi Annan’s insight into reforming the United Nations Security Council
Former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan stated, “The world is not as it was; it is a new world that requires new thinking.” This highlights the need for reform to make the UNSC more representative of today’s geopolitical landscape.
1.4.3 – How the United Nations International Court of Justice resolves international disputes
The International Court of Justice (ICJ), located in The Hague, is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations. Established in 1945, the ICJ settles legal disputes between states and provides advisory opinions on international legal issues referred to it by the UN General Assembly, Security Council, or other specialized agencies.
The Court plays a key role in the development of international law and in resolving disputes through legal means rather than military confrontation. Its work contributes to global stability by offering a peaceful forum for conflict resolution.
1.4.3.1 – Franklin D. Roosevelt’s vision of peace through the United Nations International Court of Justice
President Franklin D. Roosevelt noted, “The future belongs to those who believe in the beauty of their dreams.” This underscores the importance of envisioning a world where law and justice prevail over conflict.
1.4.4 – How the United Nations Secretariat supports international diplomacy
The UN Secretariat, headed by the Secretary-General, is responsible for the day-to-day operations of the United Nations. It implements decisions made by the General Assembly and Security Council, conducts studies, prepares reports, and provides services to other UN bodies.
1.4.4.1 – António Guterres’ vision of global unity and the United Nations Secretariat’s role
The Secretary-General is often regarded as the “face of the UN” and plays a key role in diplomacy and international negotiations. António Guterres, the current Secretary-General, has emphasized global solidarity, particularly in times of crisis. His statement, “We are all in this together,” reflects the interconnectedness of global challenges.
1.4.5 – How Specialized Agencies Support the United Nations Mission
Beyond the main UN bodies, several specialized agencies and programs address specific global issues, including:
1.4.5.1 – WHO’s Role in Global Public Health and Disease Prevention (WHO)
Focuses on public health and disease prevention.
1.4.5.2 – United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
Promotes education, science, and culture.
1.4.5.3 – United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
Improves the lives of children and mothers worldwide.
1.4.5.4 – How WFP Addresses Hunger and Emergency Relief Globally
Addresses global hunger and food security.
These agencies operate independently but collaborate with the UN to fulfill their mandates. For example, UNICEF’s work in education and health supports the UN’s broader goals of sustainable development and human rights, highlighting the interconnectedness of the UN’s work.
1.4.6 – How UN Regional Commissions Foster Development in Global Regions
The UN operates several regional commissions to address specific needs in different parts of the world. These commissions provide policy analysis, technical assistance, and capacity-building support to help member states with their development efforts.
For example, the Economic Commission for Africa (ECA) focuses on sustainable development in African nations, while the Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) addresses challenges specific to Asia and the Pacific regions. These commissions foster cooperation and knowledge-sharing, reinforcing the UN’s commitment to regional development.
1.4.7 – How Civil Society Organizations Impact UN Policy and Global Goals
Civil society organizations (CSOs) play a crucial role in the UN’s ecosystem. These non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and advocacy groups work with the UN to represent the interests of communities and promote transparency and accountability.
The UN values its collaboration with CSOs, as these organizations often provide vital on-the-ground insights and expertise.
1.4.7.1 – Ban Ki-moon’s Vision of Working Together for Global Development
Former UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon stated, “We need to work together to help people build their futures.” This collaboration underscores the importance of grassroots movements and local perspectives in achieving the UN’s objectives.
1.4.8 – How the UN’s Structure Promotes International Cooperation
The structure and key bodies of the UN are central to its mission of promoting peace, security, and sustainable development worldwide. Each body plays a unique role in advancing the UN’s goals while reflecting the diversity of its member states. Understanding this structure helps individuals appreciate the complexities of global governance and the importance of international cooperation.

United Nations declaration highlighting its founding principles and dedication to global peace and cooperation.
1.5 – How the United Nations Contributes to Global Peace and Stability
Discover how the United Nations promotes global peace and stability through diplomacy, conflict resolution, and humanitarian efforts to create a safer world.
The United Nations and Global Peacekeeping initiatives are central to the UN’s mission of maintaining peace and security worldwide. Understanding the UN’s role in peacekeeping is crucial, especially as global conflicts and crises continue to emerge. People seek insights into how the UN deploys peacekeeping forces, their impact on local communities, and the challenges they face in a complex global landscape.
The importance of peacekeeping reflects the UN’s commitment to conflict resolution and the collective desire for a safer, more stable world.
1.5.1 – What is the Role of UN Peacekeeping in Conflict Resolution?
UN peacekeeping missions help countries transition from conflict to peace. These operations involve monitoring ceasefires, protecting civilians, disarming combatants, and supporting political processes. The aim is to create a secure environment conducive to rebuilding and recovery.
Peacekeeping forces, deployed at the request of member states, include soldiers, police, and civilian personnel from various countries, working together to promote stability and protect human rights.
1.5.1.1 – Dag Hammarskjöld’s View on Peacekeeping
Former UN Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjöld famously said, “Peacekeeping is not a soldier’s job; it is a politician’s job.” This highlights that military presence is only part of the equation, with political will and diplomatic engagement essential for success.
1.5.2 – How UN Peacekeeping Has Adapted Over Decades to Global Conflicts
The history of UN peacekeeping began in 1948 with military observers deployed to the Middle East to monitor a ceasefire between Israel and its neighbors. Since then, peacekeeping has evolved in response to global conflicts.
In the 1990s, challenges during the Rwandan Genocide and the Balkan Wars revealed the limitations of peacekeeping efforts, leading to reforms. Today, over 12 peacekeeping missions are active, with more than 100,000 personnel deployed worldwide, addressing issues such as ceasefires, elections, and infrastructure rebuilding.
1.5.3 – How UN Peacekeeping Follows Core Principles for Effective Missions
UN peacekeeping operations follow core principles that ensure missions are ethical and effective
1.5.3.1 – Why Consent is Crucial for Successful UN Peacekeeping Efforts
Peacekeeping operations require the consent of the conflicting parties, ensuring neutrality and credibility.
1.5.3.2 – Why UN Peacekeeping Requires Impartiality in Conflict Zones
Peacekeepers must remain neutral and impartial, fostering trust among conflicting parties.
1.5.3.3 – Why Non-Use of Force is Essential for UN Peacekeeping Success
Force is only used in self-defense or to protect civilians. Peacekeepers primarily serve as a stabilizing presence, not combatants.
These principles, outlined in the UN Charter, are essential for the legitimacy and success of peacekeeping efforts.
1.5.4 – Understanding the Financial and Logistical Challenges of UN Peacekeeping
While many peacekeeping missions have succeeded, significant challenges remain
1.5.4.1 – How Funding and Resources Affect the Success of UN Peacekeeping
Peacekeeping operations require substantial financial and logistical support, which can be inconsistent.
1.5.4.2 – Why Complex Conflicts Are a Major Challenge for UN Peacekeepers
Many modern conflicts are multifaceted, involving numerous actors and requiring nuanced approaches. Peacekeepers must navigate local dynamics while remaining impartial.
1.5.4.3 – How the Safety of Peacekeepers Affects the Success of Missions
Peacekeepers often operate in hostile environments, making their safety a key concern for the UN.
Calls for reform continue to address these challenges. As former U.S. President Barack Obama stated, “The United States is not just a spectator on the sidelines; we are active players on the world stage.” This reflects the need for international collaboration to support peacekeeping.
1.5.5 – Examples of Effective UN Peacekeeping Missions and Their Impact
1.5.5.1 – Successful Peacekeeping Efforts in Liberia After Civil War (UNMIL)
Deployed in 2003, UNMIL helped stabilize Liberia after its civil war, disarming combatants, supporting democratic elections, and rebuilding infrastructure, ultimately leading to a peaceful transition.
1.5.5.2 – Challenges and Successes of UN Peacekeeping in Mali (MINUSMA)
Launched in 2013, MINUSMA supports political processes in Mali and protects civilians. Despite significant challenges, it has contributed to stabilizing key regions and fostering dialogue.
1.5.5.3 – United Nations Peacekeeping in Cyprus (UNFICYP)
Established in 1964, UNFICYP has maintained peace in Cyprus for decades, facilitating dialogue between the Greek and Turkish communities and contributing to a more stable environment.
These case studies demonstrate the positive impact of UN peacekeeping and the importance of international collaboration in resolving conflicts.
1.5.6 – How the United States Supports United Nations Peacekeeping Missions
The United States plays a vital role in supporting UN peacekeeping through financial contributions and political engagement. As one of the largest financial contributors, the U.S. supports peacekeeping missions globally, underscoring its commitment to international stability.
U.S. military personnel and resources often support UN missions, reflecting the interconnectedness of national and global security.
1.5.6.1 – John F. Kennedy’s Perspective on Global Peacekeeping Efforts
President John F. Kennedy once said, “Peace is a daily, a weekly, a monthly process, gradually changing opinions, slowly eroding old barriers.” This emphasizes the need for sustained engagement in promoting global peace through collaborative efforts.
1.5.7 – How UN Peacekeeping Will Adapt to Future Global Conflicts
The future of UN peacekeeping will be shaped by evolving conflicts, shifting international politics, and increased collaboration with regional organizations.
The UN is exploring innovative approaches, such as leveraging technology for improved situational awareness and enhancing peacekeeper training. There’s also a growing focus on the inclusion of women in peacekeeping, recognizing their unique perspectives and contributions.
As global peacekeeping evolves, the UN must adapt to meet new challenges. Collaboration among member states and stakeholders will be essential in crafting effective responses.
1.5.8 – Summary of UN Peacekeeping Missions and Their Role in Global Peace
The United Nations and Global Peacekeeping initiatives are essential for promoting international stability and peace. Understanding the structure, challenges, and successes of UN peacekeeping highlights the complexities of global governance and the crucial role international cooperation plays in addressing conflicts.

Image depicting the Preamble to the United Nations Charter, which outlines the foundational principles of global peace, cooperation, and human rights.
1.6 – How the United Nations Promotes Human Rights Worldwide
Discover how the United Nations protects human rights worldwide through advocacy, policies, and initiatives that promote freedom, equality, and justice for all.
The relationship between the United Nations and human rights is central to understanding the UN’s mission and impact on global society. Established after World War II, the UN aimed to promote peace and security, soon recognizing that achieving these goals required ensuring the fundamental human rights of all individuals. This connection has evolved into a comprehensive framework designed to uphold dignity, freedom, and justice for every person, regardless of nationality, race, or beliefs.
As interest in human rights grows, many seek to understand the mechanisms the UN uses to protect these rights, including significant human rights treaties, the role of various UN agencies, and how these efforts are enforced. Additionally, understanding historical contexts, landmark declarations, and ongoing challenges faced by the UN is crucial for those engaged in social justice and international law.
1.6.1 – How the United Nations Shaped Modern Human Rights Law
The UN’s focus on human rights began with the adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) in 1948. Drafted in the aftermath of World War II, this landmark document laid the foundation for modern human rights law, articulating a broad range of rights and freedoms that all individuals are entitled to. Eleanor Roosevelt, who played a pivotal role in drafting the UDHR, famously stated, “Where, after all, do universal human rights begin? In small places, close to home—so close and so small that they cannot be seen on any maps of the world.”
The UDHR’s adoption marked a critical turning point, establishing a universal standard that countries around the globe would strive to achieve. It includes civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights, reflecting the understanding that human dignity is a multifaceted concept requiring a comprehensive approach.
1.6.2 – Major UN Human Rights Treaties and Conventions Explained
Following the UDHR, the UN developed numerous treaties and conventions aimed at protecting specific rights. Some of the most significant include
1.6.2.1 – How the ICCPR Shapes Global Human Rights Standards
Adopted in 1966, this treaty commits signatory states to respect civil and political rights, including the right to life, freedom of speech, and equality before the law.
1.6.2.2 – How the ICESCR Enhances Global Human Rights Protection
Also adopted in 1966, this covenant focuses on the rights necessary for individuals to live with dignity, such as the rights to work, health, education, and an adequate standard of living.
1.6.2.3 – How CEDAW Protects Women’s Rights on the Global Stage
This 1979 treaty addresses discrimination against women and aims to achieve gender equality.
1.6.2.4 – How the CRC Protects Children’s Rights Worldwide
Adopted in 1989, the CRC sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health, and cultural rights of children.
These instruments demonstrate the UN’s commitment to creating a comprehensive legal framework for protecting human rights globally. They serve as a basis for accountability, enabling individuals and groups to challenge violations and seek justice.
1.6.3 – How UN Agencies Protect and Promote Human Rights Globally
Several UN agencies and bodies play critical roles in advancing human rights, each with its own focus and mandate:
1.6.3.1 – How the UNHRC Works to Address Global Human Rights Violations
Established in 2006, the UNHRC addresses human rights violations and makes recommendations to promote and protect rights globally. The Council’s Universal Periodic Review process evaluates the human rights records of all UN member states, ensuring accountability.
1.6.3.2 – How the OHCHR Monitors and Protects Global Human Rights
The OHCHR supports the UNHRC and works on the ground to protect human rights through advocacy, monitoring, and reporting on violations. The High Commissioner plays a key role in promoting international human rights standards and responding to crises.
1.6.3.3 – How UNICEF Ensures Human Rights for Every Child Worldwide
Focused on children’s rights, UNICEF works to ensure every child enjoys a safe and healthy life. Its programs address education, nutrition, and protection from violence and exploitation.
1.6.3.4 – How UN Women Works to Empower Women and Eliminate Discrimination
Established in 2010, this entity focuses on gender equality and the empowerment of women, working to eliminate discrimination and violence against women and promote equal participation in all areas of life.
These agencies collaborate with governments, civil society, and international organizations to foster a culture of respect for human rights worldwide.
1.6.4 – Challenges facing human rights protection by the United Nations
Despite progress, the UN faces significant challenges in the realm of human rights
1.6.4.1 – How political resistance impacts UN human rights missions
Many countries resist international scrutiny and accountability, often labeling UN interventions as infringements on sovereignty. This resistance can impede efforts to address violations effectively.
1.6.4.2 – How UN responds to conflicts exacerbating human rights violations
Ongoing conflicts, such as those in Syria and Yemen, exacerbate human rights violations and complicate the UN’s ability to respond. Civilians often bear the brunt of violence and instability.
1.6.4.3 – How digital technology impacts human rights under UN protection
New challenges, such as the rise of digital technologies and their implications for privacy and freedom of expression, require the UN to adapt its human rights framework. The increasing relevance of climate change also threatens human rights, particularly for vulnerable populations.
1.6.4.3.1 – Ban Ki-moon’s vision on human rights and environmental sustainability
Former UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon noted, “We are the last generation that can prevent irreparable damage to our planet.” This underscores the interconnectedness of human rights, environmental sustainability, and global stability.
1.6.5 – UN case studies on human rights protection around the world
1.6.5.1 – Myanmar’s human rights violations and the UN’s stance
The UN has condemned the military’s actions against the Rohingya population, which have been described as ethnic cleansing. The UN continues to advocate for accountability and the rights of displaced persons.
1.6.5.2 – United Nations initiatives to end violence against women
The UN has launched initiatives like the UNiTE to End Violence against Women campaign, raising awareness and mobilizing action to combat gender-based violence globally.
1.6.5.3 – The United Nations and its advocacy for refugees worldwide
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) works to protect the rights of refugees and displaced persons. The Global Compact on Refugees, endorsed in 2018, aims to improve responses to large refugee movements.
These case studies illustrate the UN’s proactive efforts to uphold human rights amid complex global challenges.
1.6.6 – How NGOs and activists support UN human rights goals
Civil society organizations play a critical role in holding governments accountable and advocating for human rights. NGOs, grassroots movements, and activists are essential partners in the UN’s efforts to promote human rights.
The UN often collaborates with these organizations to gather information, develop policies, and implement programs. By amplifying the voices of marginalized communities, civil society helps ensure that human rights remain at the forefront of global discussions.
1.6.6.1 – MLK’s vision of justice in the context of UN human rights work
Martin Luther King Jr. said, “Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere.” This quote underscores the importance of collective action in the fight for human rights and the interconnectedness of struggles worldwide.
1.6.7 – How the United Nations is adapting to future human rights challenges
The future of human rights at the UN will depend on its ability to adapt to emerging challenges and the commitment of member states to uphold their obligations. Key areas of focus include:
1.6.7.1 – Strengthening UN accountability for human rights violations
Ensuring that perpetrators of human rights violations are held accountable remains a priority. Enhancing the capacity of the UN and its agencies to investigate and respond to violations is crucial.
1.6.7.2 – How the UN promotes inclusivity for marginalized communities
Emphasizing the inclusion of diverse voices, particularly marginalized communities, will be essential for developing effective policies and programs that address the unique challenges faced by various groups.
1.6.7.3 – Integrating human rights with sustainable development goals at the UN
The UN’s commitment to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development underscores the importance of integrating human rights into development efforts. Addressing poverty, inequality, and environmental sustainability is crucial for ensuring the protection of human rights for all.
As the world faces unprecedented challenges, the UN’s dedication to promoting and protecting human rights will be more critical than ever.
1.6.8 – How the UN upholds human rights in global governance
The United Nations and Human Rights represent a fundamental aspect of global governance aimed at ensuring dignity, freedom, and justice for all individuals. Understanding the historical context, key instruments, and ongoing challenges highlights the UN’s vital role in shaping a more just and equitable world.
1.7 – How the United Nations’ SDGs Address Global Challenges and Promote Sustainability
Discover how the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) tackle global challenges and drive sustainability for a better future worldwide.
The United Nations introduced the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015 as part of a global initiative to tackle pressing challenges. Embedded within the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, these goals focus on eradicating poverty, safeguarding the environment, and promoting widespread prosperity. With 17 overarching goals and 169 specific targets, the SDGs encompass a diverse range of social, economic, and environmental priorities, laying the groundwork for a more just and sustainable future.
1.7.1 – Why the United Nations Created the SDGs
The SDGs emerged from the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development, known as Rio+20, held in 2012. This conference emphasized the need for a new framework to succeed the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), which focused primarily on poverty reduction from 2000 to 2015. While the MDGs achieved some success, they were criticized for their narrow scope.
The SDGs expand on the lessons learned from the MDGs, addressing a wider array of interconnected challenges.
1.7.1.1 – Ban Ki-moon’s Urgent Call for Action to The Last Generation to Save the Planet
Former UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon noted, “We are the last generation that can prevent irreparable damage to our planet.” This reflects the urgency of the SDGs in tackling global issues such as poverty, inequality, and climate change.
1.7.2 – 17 Global Goals of the United Nations for Sustainable Development
The SDGs consist of 17 goals, each with specific targets aimed at solving global issues. Here is an overview
1.7.2.1 – No poverty goal United Nations and its global impact
End poverty in all its forms everywhere.
1.7.2.2 – How the United Nations is working to end hunger globally
Eliminate hunger, ensure reliable access to nutritious food, and support sustainable farming practices.
1.7.2.3 – Promoting good health and well-being under the United Nations SDGs
Foster good health and enhance well-being for individuals of all ages.
1.7.2.4 – United Nations goal to provide quality education for all
Guarantee accessible, high-quality education for everyone while fostering lifelong learning opportunities.
1.7.2.5 – UN strategies for promoting gender equality globally
Promote gender equity and strengthen the rights and opportunities of all women and girls.
1.7.2.6 – United Nations efforts to provide clean water for all
Guarantee access to safe water and effective sanitation for everyone while promoting sustainable management practices.
1.7.2.7 – Affordable and renewable energy solutions in UN Sustainable Development Goals
Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all.
1.7.2.8 – Promoting decent work and economic growth through the United Nations
Encourage long-term, inclusive, and sustainable economic development while ensuring full, productive employment and fair working conditions for everyone.
1.7.2.9 – Industry innovation and infrastructure goals of the United Nations
Build resilient infrastructure, promote sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation.
1.7.2.10 – Ending inequality and promoting inclusivity through UN SDGs
Reduce inequality within and among countries.
1.7.2.11 – Building sustainable cities through the United Nations SDGs
Ensure that urban areas and human communities are welcoming, secure, adaptable, and environmentally sustainable.
1.7.2.12 – Responsible consumption and sustainable production through UN SDGs
Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns.
1.7.2.13 – How the United Nations is addressing climate change globally
Take immediate steps to address climate change and mitigate its effects.
1.7.2.14 – Sustainable oceans and seas under the United Nations goals
Protect and responsibly manage oceans, seas, and marine resources to support long-term sustainable development.
1.7.2.15 – United Nations goal for protecting life on land and biodiversity
Safeguard, revitalize, and encourage the responsible use of land-based ecosystems, ensure sustainable forest management, prevent desert expansion, and preserve biodiversity.
1.7.2.16 – Promoting peace and justice through the United Nations SDGs
Foster harmonious and inclusive communities, ensure equal access to justice for everyone, and establish transparent, responsible institutions.
1.7.2.17 – United Nations partnerships for achieving global SDGs
Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize global partnerships for sustainable development.
These interconnected goals emphasize the need for a holistic approach to sustainable development.
1.7.3 – Why the SDGs are crucial for global development
The SDGs represent a collective effort to transform the world. They are designed to be inclusive, universal, and integrated, ensuring that no one is left behind. Key reasons the SDGs are crucial include:
1.7.3.1 – How the United Nations’ SDGs framework drives international cooperation
The SDGs provide a shared framework for governments, civil society, and private organizations to align efforts toward common goals.
1.7.3.2 – SDGs and Policymaking under the United Nations
They offer guidelines for policymakers to create inclusive and sustainable policies addressing the root causes of global challenges.
1.7.3.3 – Resource mobilization for SDGs by the United Nations
The SDGs attract investment and innovation, encouraging sustainable development funding across sectors.
1.7.3.4 – How the United Nations tracks global progress on SDGs
Countries can track progress through measurable indicators, ensuring accountability and transparency.
1.7.3.5 – Global collaboration on SDGs through the United Nations
The SDGs promote international cooperation, recognizing that global challenges, like climate change and pandemics, require collective action.
1.7.4 – How citizens contribute to SDGs through the United Nations
Interest in the SDGs is growing, with more citizens seeking ways to contribute. Key actions include:
1.7.4.1 – Community-driven SDG projects endorsed by the United Nations
Engage with local organizations working towards specific SDGs, such as food banks for Zero Hunger or environmental groups for Climate Action.
1.7.4.2 – How the United Nations promotes SDG awareness globally
Advocate for policies that support sustainability, such as climate action or healthcare access.
1.7.4.3 – How the United Nations encourages sustainable consumption habits
Adopt sustainable practices like reducing waste, conserving water, and supporting ethical consumption.
1.7.4.4 – Learning about SDGs through United Nations resources
Participate in educational programs to raise awareness of global sustainability challenges.
The internet is a valuable resource for learning about the SDGs, offering articles, webinars, and community events.
1.7.5 – Inspirational SDG quotes endorsed by the United Nations
Inspirational quotes can motivate action toward the SDGs. Here are a few
1.7.5.1 – Robert Swan’s quote on environmental responsibility and SDGs
“The greatest threat to our planet is the belief that someone else will save it.” — Robert Swan, polar explorer.
1.7.5.2 – Ban Ki-moon’s perspective on sustainable development and SDGs
“Sustainable development is the pathway to the future we want for our world.” — Ban Ki-moon, former UN Secretary-General.
1.7.5.3 – Native American proverb on sustainability and SDGs
“We do not inherit the earth from our ancestors; we borrow it from our children.” — Native American proverb.
These quotes underscore our collective responsibility to care for the planet and future generations.
1.7.6 – Challenges in Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Despite the SDGs’ ambitious agenda, there are challenges and critiques
1.7.6.1 – SDG Implementation Gaps in Developing Countries
Many countries face difficulties in effectively implementing the goals due to limited resources, political will, or capacity.
1.7.6.2 – Data Gaps in Monitoring Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Accurate data is vital for monitoring progress, but many regions, particularly in developing countries, lack robust data systems.
1.7.6.3 – Inclusive Development in the Context of SDGs
Critics argue that the SDGs may not fully address the needs of marginalized communities, calling for greater inclusivity in the development process.
1.7.6.4 – Sustainability vs. Growth in SDG Debate
Debates continue over balancing economic growth with sustainable development, with calls for innovative approaches that harmonize these priorities.
Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensuring the SDGs fulfill their promise of a more equitable and sustainable world.
1.7.7 – How Individuals Contribute to Achieving Sustainable Development Goals
Individuals can play a key role in achieving the SDGs through advocacy, education, and personal choices. Here are some ways to get involved
1.7.7.1 – How to Raise Awareness of the SDGs
Learn about the SDGs and share that knowledge with others to raise awareness and inspire action.
1.7.7.2 – How Volunteering Supports SDGs
Join local organizations working on sustainable development projects related to specific SDGs.
1.7.7.3 – How to Support Sustainable and Ethical Businesses
Support companies that prioritize sustainability and ethical practices.
1.7.7.4 – How to Advocate for Sustainable Development Goals
Promote policies that align with the SDGs at local, state, and national levels.
As Mahatma Gandhi said, “Be the change that you wish to see in the world.” Small actions can lead to collective impacts.
1.7.8 – Why SDGs Are Critical for Global Sustainability
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) represent a transformative agenda addressing the world’s most pressing challenges. By understanding their context and importance, and recognizing the role of individuals in achieving these goals, we can work toward a sustainable and equitable future. Engaging with the SDGs empowers individuals to make informed decisions and fosters a sense of global responsibility.
1.8 – How America Shapes Global Initiatives in the United Nations
Discover how America influences global initiatives in the United Nations, shaping policies, diplomacy, and international cooperation to drive key global decisions.
The United Nations (UN), founded in 1945, serves as a critical platform for promoting international cooperation, peace, and development. The United States, as a founding member, has been influential in shaping the UN’s agenda and addressing global challenges. From human rights advocacy to climate change and conflict resolution, the U.S. has been at the forefront of many key initiatives.
Understanding America’s role in the UN is essential, especially in an era of global interdependence. This knowledge extends beyond politics to practical engagement, as citizens increasingly seek ways to address international issues that impact their communities. America’s involvement in the UN reflects its moral responsibility as a global leader.
1.8.1 – How America helped establish the United Nations after WWII
The U.S. played a key role in establishing the UN after World War II, recognizing the need for an international body to prevent future conflicts and promote peace. The UN Charter was signed on June 26, 1945, with President Harry S. Truman championing the formation of a strong organization for global cooperation.
1.8.1.1 – Harry S. Truman’s vision for the United Nations
Truman famously stated, “The UN was not created to take mankind to heaven, but to save humanity from hell.” This quote underscores the UN’s mission to address global challenges and the significant role the U.S. plays in this effort.
1.8.2 – How the U.S. has supported United Nations peacekeeping
The United States has made substantial contributions to the UN in several key areas
1.8.2.1 – How the U.S. funds United Nations peacekeeping missions
The U.S. is one of the largest financial contributors to the UN, providing around 22% of its regular budget and 28% of the peacekeeping budget. This financial commitment demonstrates America’s dedication to international peace and stability.
1.8.2.2 – How the U.S. shapes UN resolutions through leadership positions
The U.S. has held various leadership roles within the UN, including positions in the Security Council and General Assembly. U.S. ambassadors have been instrumental in shaping discussions and resolutions on security, human rights, and humanitarian issues.
1.8.2.3 – How U.S. troops support United Nations peacekeeping efforts
The U.S. has actively supported UN peacekeeping missions by contributing troops, resources, and training. These efforts aim to maintain peace and security in conflict-affected regions, reinforcing America’s commitment to global stability.
1.8.3 – How America advanced the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The U.S. has been a strong advocate for human rights within the UN framework. The adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948 marked a milestone in promoting individual freedoms worldwide, with the U.S. playing a key role in drafting it. The declaration emphasizes civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights.
1.8.3.1 – Universal human rights and the U.S. role in shaping them
In a speech to the UN General Assembly, Eleanor Roosevelt, a key figure in the declaration’s creation, said, “Where, after all, do universal human rights begin? In small places, close to home—so close and so small that they cannot be seen on any map of the world.” This quote reinforces the importance of protecting human rights at all levels, illustrating the U.S. commitment to these values globally.
1.8.4 – How the U.S. contributes to conflict resolution through the UN
The UN serves as a platform for tackling global challenges, with the U.S. taking a leadership role in several areas:
1.8.4.1 – How the U.S. supports global climate change efforts through the UN
The U.S. has actively engaged in discussions and initiatives related to climate change, including the Paris Agreement. By advocating for ambitious climate goals, the U.S. aims to lead efforts in combating global warming.
1.8.4.2 – United States leadership in global health initiatives within the UN
The U.S. has been integral in global health initiatives through the UN, focusing on combating infectious diseases and promoting health equity. Programs like the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria demonstrate America’s commitment to improving global health outcomes.
1.8.4.3 – How the U.S. helps resolve conflicts through the United Nations
Through diplomatic efforts and peacekeeping missions, the U.S. has contributed to conflict resolution and peacebuilding worldwide. The UN’s role in mediating conflicts is crucial, with the U.S. often playing a leading role in these efforts.
1.8.5 – Why the United States faces challenges in the UN
Despite its strong presence, the U.S. faces challenges and critiques regarding its role
1.8.5.1 – Debate on U.S. isolationism vs global leadership in the United Nations
There is ongoing debate over the balance between isolationism and global leadership. Some advocate for reduced U.S. involvement in international affairs, while others stress the importance of continued engagement in global issues.
1.8.5.2 – Why the United Nations is criticized for its effectiveness
Critics point to perceived inefficiencies within the UN, questioning its ability to effectively address global challenges. This critique influences U.S. policy and funding decisions regarding the UN.
1.8.5.3 – How U.S. human rights record impacts its UN policy
The U.S. has faced scrutiny over its own human rights record, particularly concerning its foreign policies. Critics argue that the U.S. should uphold the same human rights standards it advocates for globally, highlighting the need for consistency and accountability.
1.8.6 – How U.S. citizens engage with United Nations issues
As more citizens seek information online, interest in engaging with the UN’s work has grown. Many are focused on
1.8.6.1 – How the United Nations addresses global climate change and human rights
Understanding how the UN addresses climate change, human rights abuses, and poverty.
1.8.6.2 – How to advocate for United Nations initiatives on human rights
Finding ways to support policy changes aligned with UN initiatives.
1.8.6.3 – How global challenges impact local U.S. communities
Learning how global challenges affect local communities and what actions can be taken.
Educational resources, online platforms, and social media are essential for fostering public awareness and engagement.
1.8.7 – Famous quotes advocating U.S. leadership in the United Nations
Several historical quotes inspire engagement with international issues and underscore the U.S. role in the UN
1.8.7.1 – General Douglas MacArthur’s quote on avoiding war and the UN’s peace mission
“The only way to win a war is to avoid it.” — General Douglas MacArthur, highlighting the UN’s peace-promoting mission.
1.8.7.2 – Samantha Power’s call to action for human rights and U.S. advocacy in the UN
“We cannot be silent. We must not be silent. We must speak up.” — Former UN Ambassador Samantha Power, emphasizing the moral obligation to advocate for human rights and justice.
1.8.8 – The U.S. responsibility in the United Nations and global challenges
The United States’ role in the United Nations is multifaceted, encompassing financial support, leadership, human rights advocacy, and active engagement in global challenges. As a founding member and one of the largest contributors, the U.S. has a unique responsibility to uphold the values and principles of the UN. By fostering public awareness, U.S. citizens can contribute to the UN’s mission and help shape a more peaceful and just world.
1.9 – Why the United Nations struggles with international conflicts
Discover why the United Nations faces challenges in resolving global conflicts, from political divisions to enforcement limitations, and what this means for world peace.
The United Nations (UN) has been a central platform for global diplomacy, humanitarian efforts, and peacekeeping since its establishment in 1945. However, as the world evolves and new challenges emerge, the UN has faced increasing criticism regarding its effectiveness and relevance. This article explores the primary criticisms and challenges the UN faces today, providing insight into various perspectives and historical contexts.
1.9.1 – History of Criticism towards the United Nations
Since its founding, the UN has been subject to scrutiny. Its primary goal is to foster international cooperation and prevent conflicts, yet critics argue that it has often fallen short of these objectives. Events like the Rwandan Genocide in 1994 and the ongoing conflicts in Syria and Yemen have raised questions about the UN’s ability to respond effectively to humanitarian crises and protect human rights.
1.9.1.1 – Kofi Annan’s view on the United Nations’ role in global conflicts
Former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan remarked, “The UN is not the world’s policeman. The UN is an organization of member states, but it has to operate in a world where the interests of the powerful often override those of the weak.” This quote highlights the tension within the organization, where the interests of member states can impact its effectiveness.
1.9.2 – How the UN Security Council structure impacts international relations
One of the primary criticisms of the UN revolves around its structure, particularly the power dynamics within the Security Council.
1.9.2.1 – How veto power in the UN Security Council affects resolutions
The five permanent members of the Security Council—United States, Russia, China, France, and the United Kingdom—hold veto power, allowing them to block resolutions. This structure has caused frustration, especially in addressing global conflicts. For example, Russia’s veto of UN resolutions related to the Syrian Civil War has sparked debates about the UN’s ability to maintain international peace.
1.9.2.2 – Challenges posed by UN bureaucracy on global peacekeeping
Critics also point to the UN’s bureaucratic nature as a challenge. With 193 member states and numerous specialized agencies, decision-making can be slow and cumbersome. This complexity often leads to inefficiencies, making it difficult to respond quickly to emerging crises.
1.9.3 – How lack of accountability harms the UN’s peacekeeping efforts
1.9.3.1 – How the UN’s lack of accountability affects global trust
The UN has been criticized for its lack of accountability mechanisms. When failures occur, such as in peacekeeping missions that do not fulfill their mandates, it can be difficult to hold the organization or specific nations accountable. This lack of accountability can undermine trust in the UN as a reliable mediator and peacekeeper.
1.9.3.2 – What reforms are needed for the United Nations to stay relevant
Reform advocates argue for changes to make the UN more effective and representative. Proposals have included expanding the Security Council’s permanent membership to better reflect the geopolitical landscape, addressing the imbalance of power, and streamlining its operations to enhance efficiency.
1.9.3.2.1 – What Linda Thomas-Greenfield says about global realities
Former US Ambassador to the UN, Linda Thomas-Greenfield, has stated, “We need a UN that reflects the realities of today’s world, not the world of 1945.” This sentiment resonates with many who believe the UN must adapt to current global dynamics.
1.9.4 – Why the UN faces challenges in enforcing human rights
While the UN is a staunch advocate for human rights, its ability to enforce these rights has been called into question.
1.9.4.1 – Why the UN Human Rights Council is often seen as politicized
The UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC) has faced allegations of bias and ineffectiveness. Critics argue that the Council often focuses disproportionately on specific countries while ignoring violations in others, leading to accusations of politicization. For example, the UNHRC has been criticized for its consistent scrutiny of Israel while overlooking human rights abuses in countries like China and Venezuela.
1.9.4.2 – Why UN resolutions often fail to protect human rights effectively
Even when the UN passes resolutions aimed at protecting human rights, their implementation can be inconsistent. Member states may ignore these resolutions, undermining the UN’s authority and effectiveness.
1.9.4.2.1 – What Barack Obama said about the United Nations’ role in world leadership
Former President Barack Obama once said, “Real change will come when we acknowledge the simple truth: that we can’t be a world leader if we’re not willing to lead.” This reinforces the need for accountability and action.
1.9.5 – How the United Nations handles global health crises
The UN’s effectiveness has been challenged by significant global crises, including
1.9.5.1 – How the United Nations managed global pandemic responses
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted both the strengths and weaknesses of the UN. While the World Health Organization (WHO) played a crucial role in coordinating global responses, critics pointed to delays and communication failures that hindered early responses to the virus.
1.9.5.2 – How the United Nations is addressing climate change issues
As climate change poses an existential threat, the UN has sought to mobilize international action through initiatives like the Paris Agreement. However, critics argue that more needs to be done to enforce commitments and hold nations accountable for their contributions to global warming.
1.9.5.2.1 – Ban Ki-moon’s View on addressing Climate Change and global poverty
Former United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon highlighted this urgency by asserting that protecting our planet, alleviating poverty, and fostering economic progress are all interconnected battles. He stressed the importance of linking climate change, water shortages, energy deficits, public health, food stability, and gender equality, emphasizing that solutions should address multiple challenges simultaneously. This comprehensive perspective reinforces the deep interdependence of global issues.
1.9.6 – How misinformation affects the United Nations’ reputation
In the digital age, public perception of the UN is heavily influenced by online information and misinformation. Many individuals seek to understand the UN’s role and its impact on global issues through news articles, social media, and online discussions. However, misinformation can shape negative perceptions of the organization, leading to calls for its defunding or dismantling.
To combat misinformation, the UN and member states must engage transparently with the public, providing accurate information and promoting awareness of the UN’s achievements and ongoing challenges.
1.9.7 – How the United Nations can adapt to contemporary global challenges
As the United Nations faces criticism and challenges, it remains an essential institution for fostering international cooperation and addressing global issues. Reforming its structures, enhancing accountability, and adapting to contemporary challenges will be crucial for ensuring its relevance in the 21st century.
By understanding the criticisms and challenges the UN faces, individuals can engage in informed discussions and support initiatives aimed at strengthening global governance.
1.10 – How the United Nations Addresses Key Global Issues
Discover how the United Nations tackles global challenges like peace, climate change, and human rights, shaping a better future through international cooperation.
The United Nations (UN), established in 1945, has been central to international diplomacy. Created to promote cooperation among countries, it addresses global issues ranging from peace and security to development and human rights. Understanding the UN’s impact on global challenges is essential in today’s rapidly changing world. This article explores the UN’s role in tackling various global challenges, providing historical context, insights, and key quotes.
1.10.1 – How the United Nations Impacts Global Issues and Peace Efforts
The UN is widely recognized for its peacekeeping efforts, deploying missions worldwide to prevent conflict and protect civilians.
1.10.1.1 – How the UN Maintains Peace in Conflict Zones Worldwide
The UN has overseen several successful peacekeeping operations, such as in Liberia and Sierra Leone, which helped stabilize war-torn countries. The United Nations Multidimensional Integrated Stabilization Mission in Mali (MINUSMA) also reflects the UN’s ongoing commitment to peace in complex environments.
1.10.1.2 – How UN Peacekeeping Missions Have Stabilized Global Conflicts
Despite successes, the UN’s peacekeeping missions have faced criticism, with challenges including resource limitations, insufficient mandates, and occasional inaction. Failures, such as during the Rwandan Genocide, raise important questions about the UN’s effectiveness.
1.10.1.2.1 – Kofi Annan’s Views on UN Peacekeeping and Global Security
Former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan remarked, “The United Nations has a responsibility to take a leading role in creating a more peaceful world.”
1.10.2 – How the United Nations Provides Aid During Global Crises
The UN plays a pivotal role in assisting during humanitarian crises caused by conflicts, natural disasters, or pandemics.
1.10.2.1 – How the UN Responds to Humanitarian Crises and Emergencies
Agencies like the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) and the World Food Programme (WFP) deliver vital humanitarian aid. For instance, during the Syrian refugee crisis, the UNHCR provided shelter, food, and medical support to displaced people.
1.10.2.2 – How the United Nations Promotes Sustainable Solutions to Crises
Beyond immediate relief, the UN works on long-term solutions to address the root causes of crises, promoting sustainable development to prevent future conflicts.
1.10.2.2.1 – Ban Ki-moon’s Quotes on UN Efforts to Combat Poverty and Climate Change
Ban Ki-moon stated, “Saving our planet, lifting people out of poverty, advancing economic growth…these are the same fight.”
1.10.3 – How the United Nations Promotes Global Sustainable Development
The UN plays a leading role in promoting sustainable development through initiatives like the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
1.10.3.1 – How the UN SDGs Address Poverty, Climate Change, and Inequality
Adopted in 2015, the SDGs comprise 17 goals aimed at eradicating poverty, addressing inequality, and combating climate change, with a target to achieve them by 2030.
1.10.3.2 – How the U.S. Supports UN Sustainable Development Goals
The SDGs are increasingly relevant in the U.S., where citizens seek to understand their country’s role in sustainable practices, renewable energy, and social equity.
1.10.3.2.1 – Barack Obama’s Views on UN Sustainability and Global Cooperation
Former President Barack Obama emphasized, “We will not be able to solve our problems without a global approach.”
1.10.4 – How the UN Leads Global Efforts to Combat Climate Change
The UN plays a central role in combating climate change, a critical global challenge.
1.10.4.1 – How the UN Facilitates Global Climate Agreements Like the Paris Accord
The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) has facilitated key agreements like the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
1.10.4.2 – How the UN Mobilizes Countries to Combat Climate Change
The UN has also spearheaded initiatives like the Climate Action Summit, encouraging countries and organizations to enhance their climate commitments.
1.10.4.2.1 – António Guterres’ Call for Urgent UN Climate Action
UN Secretary-General António Guterres has emphasized the urgency, stating, “We are in a race against time.”
1.10.5 – How the UN Promotes Global Human Rights Initiatives
The UN has long been a champion of human rights, making significant contributions to global human rights issues.
1.10.5.1 – UN human rights framework through the 1948 Declaration
Adopted in 1948, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights serves as a foundational document outlining the basic rights every human is entitled to.
1.10.5.2 – How the UN Human Rights Council addresses global abuses
The UN Human Rights Council monitors abuses and promotes accountability. However, it has faced criticism for perceived bias and inefficacy in addressing certain issues.
1.10.5.3 – Eleanor Roosevelt’s contribution to the UN human rights declaration
Eleanor Roosevelt, a key figure in drafting the Declaration, said, “Where, after all, do universal human rights begin? In small places, close to home.”
1.10.6 – How the UN supports global health through WHO
The UN, through the World Health Organization (WHO), plays a critical role in global health.
1.10.6.1 – UN’s global health efforts during COVID-19 and beyond
The WHO leads campaigns to combat pandemics, improve maternal and child health, and address diseases such as HIV/AIDS and malaria. Its response to COVID-19, including the COVAX vaccine initiative, demonstrated the UN’s commitment to global health security.
1.10.6.2 – How the UN Addresses Health Disparities Globally
The UN advocates for health equity, ensuring all individuals have access to essential healthcare services, in line with SDG Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being.
1.10.7 – How the UN promotes public awareness and education
In the digital age, the UN recognizes the importance of educating and informing the public about global issues.
1.10.7.1 – How the UN engages citizens through awareness programs
The UN promotes campaigns to raise awareness about global challenges, such as the UN’s 75th anniversary campaign, which engages citizens in discussions about global cooperation.
1.10.7.2 – How the United Nations empowers young people for change
The UN also targets youth education and empowerment to foster a generation actively involved in addressing global challenges.
1.10.8 – Why the United Nations remains vital for global peace
The United Nations remains a vital player in tackling global challenges, from peacekeeping to climate action. While it faces ongoing challenges and criticisms, its impact is undeniable. As global interconnectedness increases, understanding the UN’s role in addressing pressing issues is crucial.
By engaging with the UN’s initiatives and staying informed, individuals can contribute to creating a more effective international system. The UN’s ability to adapt to emerging challenges will determine its future relevance.
1.11 – How the United Nations continues to shape global policies
Discover how the United Nations shapes global policies, addressing key issues like climate change, human rights, and security to drive international cooperation.
The United Nations is instrumental in tackling worldwide challenges. With growing interest in international relations, it is vital to comprehend the UN’s influence on peacekeeping, humanitarian efforts, development, and human rights. Its programs not only guide global policymaking but also motivate local initiatives, bridging the gap between global concerns and community action.
In conclusion, the UN fosters cooperation and dialogue, striving for a peaceful, equitable, and sustainable world. By engaging with the UN’s work and staying informed, individuals can help advocate for positive change, contributing to the organization’s mission. Emphasizing education and awareness empowers citizens to become active participants in creating a better global future.