Benjamin Franklin
Discover the legacy of Benjamin Franklin—Founding Father, inventor, and statesman. Explore his impact on American history, innovation, and diplomacy.
1.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s role in shaping American culture
Discover how Benjamin Franklin shaped American culture through his innovations, writings, and values, leaving a lasting impact on society, education, and civic life.
Benjamin Franklin, a pivotal Founding Father, is celebrated for his diverse roles as an inventor, diplomat, and writer. His influence extended beyond politics during the American Revolution to encompass groundbreaking scientific discoveries and philosophical ideas. Franklin’s writings, such as Poor Richard’s Almanack, are treasured for their practical wisdom and insights into self-education.
1.1.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s Investment in Knowledge quote explanation
Franklin famously said, “An investment in knowledge always pays the best interest,” reflecting his belief in lifelong learning, which continues to inspire those seeking educational resources. He also valued hard work and civic responsibility, stating, “The only way to win is to work hard.” These principles remain relevant to modern audiences looking for role models who embody integrity and diligence.
1.1.2 – Exploring Benjamin Franklin’s adventurous spirit in his kite experiment
Franklin’s legacy is marked by notable events, including his iconic kite experiment, which not only advanced our understanding of electricity but also demonstrated his adventurous spirit. His enduring impact on modern thought, expressed through phrases like “Time is money,” continues to influence concepts of productivity and personal development.
This blog will explore Franklin’s political contributions, scientific achievements, and educational philosophy, providing insights into his life and lasting influence on American culture.

1.2 – How Benjamin Franklin’s Childhood Shaped His Education
Discover how Benjamin Franklin’s childhood curiosity and early experiences shaped his education, laying the foundation for his future as a renowned innovator.
Benjamin Franklin’s rise from humble beginnings to one of the most influential figures in American history is a testament to his self-education, curiosity, and perseverance. Born on January 17, 1706, in Boston, Massachusetts, he was the fifteenth of seventeen children in a family of modest means. Josiah Franklin’s father was a candle maker and hoped Benjamin would follow in his trade, but Franklin had other aspirations.
1.2.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s Early Years in Boston
Franklin’s early environment greatly influenced his intellectual development. Growing up in a Puritan household, he learned the values of hard work and religious devotion. However, it was his mother’s encouragement of reading that sparked his curiosity. Despite limited formal schooling, which lasted only two years, Franklin became an avid reader, spending much time at the local library and absorbing knowledge across various fields.
1.2.1.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s Learning Philosophy and Quotes
He famously said, “Tell me and I forget, teach me and I remember, involve me and I learn,” reflecting his belief in active learning. This drive for knowledge led him to teach himself mathematics, philosophy, and science using borrowed books.
1.2.2 – How Self-Education Shaped Benjamin Franklin’s Career
Franklin’s lack of formal education only fueled his desire to learn. By age 12, he became an apprentice to his older brother James, a printer. This exposure to literature and journalism marked the beginning of his writing career. While working in the printing shop, he wrote and published his articles, laying the foundation for his future as a writer and editor.
1.2.2.1 – How Benjamin Franklin’s Writing Shaped His Intellectual Path
Franklin’s time in the printing shop reinforced his belief in the power of the written word. He famously remarked, “In this world, nothing can be said to be certain, except death and taxes,” illustrating his understanding of human nature and societal issues, themes that would recur throughout his writings.
1.2.3 – Benjamin Franklin’s Interest in Electricity and Science
During his apprenticeship, Franklin became interested in scientific inquiry, particularly electricity, which would become central to his scientific contributions. He engaged in informal discussions with local intellectuals and sought out mentors to expand his knowledge. His passion for learning led him to establish the Junto, a club of like-minded individuals who engaged in intellectual discourse and civic engagement.
1.2.3.1 – How Benjamin Franklin Valued Education and Knowledge
Franklin’s guiding principle, “An investment in knowledge always pays the best interest,” influenced both himself and Junto members.
1.2.4 – How Benjamin Franklin’s Travels Shaped His Education
In 1723, Franklin left Boston for Philadelphia, where he continued to refine his writing and printing skills. Philadelphia, a thriving center of commerce and ideas, played a key role in his intellectual growth. Here, Franklin encountered diverse perspectives, which broadened his understanding of the world. He engaged with prominent thinkers, enriching his education and expanding his horizons.
1.2.5 – Benjamin Franklin’s Commitment to Accessible Education
Franklin’s commitment to education endured throughout his life. In 1731, he founded the Library Company of Philadelphia, the first subscription library in America, to provide access to books and resources for those unable to afford them. Franklin envisioned a society where education was accessible to all, reflecting his belief in the power of literacy.
1.2.5.1 – How Benjamin Franklin Shaped Higher Education in America
Additionally, Franklin played a key role in establishing the University of Pennsylvania in 1740. He advocated for an institution combining practical and theoretical learning, emphasizing the importance of applying knowledge in real-world settings. His influence in these educational ventures highlights his lifelong dedication to learning and civic responsibility.
1.2.6 – How Benjamin Franklin’s Writings Influenced American Thought
Franklin’s early life and education shaped his philosophical views, which often emphasized ethical behavior, personal responsibility, and knowledge. His writings encouraged self-improvement and contributing to society. He famously said, “The way to see by faith is to shut the eye of reason,” underscoring his belief in balancing faith and reason—a theme reflected in his scientific and public endeavors.
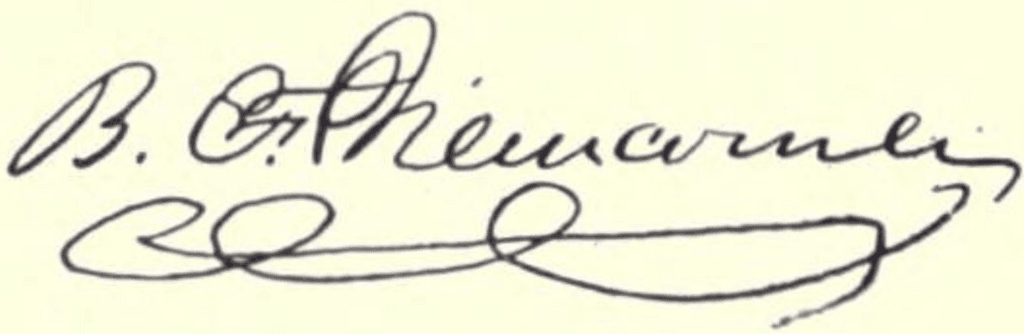
The Signature of Benjamin Franklin from Baltimore: A Profound Exploration of His History and Impact on Society (1912) highlights his significant influence and enduring legacy.
1.3 – Major achievements of Benjamin Franklin in science, politics, and education
Discover Benjamin Franklin’s groundbreaking achievements in science, politics, and education. Explore his lasting impact on American innovation and democracy.
Benjamin Franklin is a central figure in American history, known not only as a Founding Father but also for his contributions to science, politics, and education. His groundbreaking work in electricity and his diplomatic success during the American Revolution showcase his multifaceted legacy.
Franklin’s life illustrates the power of intellectual curiosity and civic engagement. He famously said, “Well done is better than well said,” emphasizing action over rhetoric. This principle guided him throughout his life as he worked to improve society and advance knowledge. His ability to blend scientific inquiry with practical application has inspired generations to seek knowledge and use it for the common good.
In this section, we will explore Franklin’s key contributions and achievements, demonstrating his lasting impact on the United States and the world.
1.3.1 – How Benjamin Franklin advanced electrical science through his experiments
Franklin’s scientific contributions, particularly in electricity, were groundbreaking. His curiosity led to experiments that revolutionized the understanding of electrical phenomena.
1.3.1.1 – How Benjamin Franklin proved lightning is electricity with the kite experiment in 1752
The Kite Experiment In 1752, Franklin famously flew a kite in a thunderstorm to demonstrate the electrical nature of lightning, proving that lightning is a form of electricity. This experiment not only advanced scientific knowledge but also paved the way for the invention of the lightning rod, which protects buildings from lightning strikes.
1.3.1.1.1 – How Benjamin Franklin’s diplomatic strategies were shaped by his quotes
Franklin’s insight, “A drop of honey catches more flies than a gallon of gall,” highlights his skill in both science and diplomacy.
1.3.1.2 – How Franklin’s electrical discoveries influenced modern science
Franklin’s Electrical Discoveries Franklin introduced key concepts to the study of electricity, including positive and negative charges, and the conservation of electric charge. His work culminated in the publication of Experiments and Observations on Electricity, a foundational text in the field. Franklin’s contributions earned him recognition in Europe, leading to his election to the Royal Society of London.
1.3.2 – Key political contributions of Benjamin Franklin in early American history
Franklin’s political achievements are equally impressive, as he played a critical role in the formation of the United States and its government.
1.3.2.1 – How Benjamin Franklin secured vital French support during the American Revolution
Diplomatic Efforts in the American Revolution During the American Revolution, Franklin served as a key diplomat in France, where he secured vital military aid and funding for the American cause. His charm and intellect helped foster key relationships with French leaders, including King Louis XVI, which led to the Treaty of Alliance in 1778.
1.3.2.2 – How Benjamin Franklin’s compromise helped form the U.S. Constitution
The Constitutional Convention Franklin was a prominent figure at the Constitutional Convention in 1787. As the oldest delegate, his support for compromise was crucial in creating the U.S. Constitution.
1.3.2.2.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s famous quote on unity at the Constitutional Convention
“We must, indeed, all hang together, or most assuredly we shall all hang separately,” emphasized the importance of unity among delegates.
1.3.3 – How Benjamin Franklin promoted education and civic engagement
Franklin’s influence extended to education and civic life, where he made lasting contributions.
1.3.3.1 – How Benjamin Franklin founded the first subscription library in America
Founding of Educational Institutions In 1731, Franklin established the Library Company of Philadelphia, the first subscription library in America. This initiative provided access to books and knowledge for many. He also played a key role in founding the University of Pennsylvania, advocating for a practical curriculum that included vocational training.
1.3.3.1.1 – How Benjamin Franklin’s education philosophy still influences today’s world
Franklin’s belief in education is captured in his words, “An investment in knowledge always pays the best interest.”
1.3.3.2 – How Benjamin Franklin promoted civic engagement through volunteerism
Promoting Civic Engagement Franklin advocated for civic responsibility and public service, founding the first volunteer fire department in Philadelphia and helping establish the first public hospital in America.
1.3.3.2.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s philosophy of combining success with social responsibility
“Doing well by doing good,” emphasized the link between personal success and social responsibility.
1.3.4 – How Benjamin Franklin’s writings shaped American thought and values
Franklin was also a prolific writer and philosopher whose works have had a lasting impact.
1.3.4.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s most influential works and publications
Writing and Publications Franklin’s writing covered a wide range of topics, including politics, science, and moral philosophy. His most famous work, Poor Richard’s Almanack, was published annually from 1732 to 1758 and became a staple in American households.
1.3.4.1.1 – The lasting influence of Benjamin Franklin’s ‘early to bed, early to rise’ quote
“Early to bed and early to rise makes a man healthy, wealthy, and wise,” continues to resonate, highlighting the value of diligence and good habits.
1.3.4.2 – How Benjamin Franklin’s philosophy influenced American ideals of liberty
Philosophical Contributions Franklin embraced Enlightenment ideals, advocating for a society based on knowledge, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. His writings explored the balance between individual rights and communal responsibilities, themes still relevant today.
1.3.4.2.1 – The influence of Benjamin Franklin’s views on justice in today’s society
“Justice will not be served until those unaffected are as outraged as those who are” reflects his commitment to social equity.
1.3.5 – The lasting legacy of Benjamin Franklin in American culture and politics
Franklin’s contributions have had a profound impact on American society and beyond. His legacy inspires individuals to pursue knowledge, engage in civic life, and strive for a better world.
1.3.5.1 – How Benjamin Franklin’s life continues to inspire future generations
Inspiring Future Generations Franklin’s life exemplifies self-improvement, hard work, and civic duty, inspiring countless individuals to seek education and contribute positively to society. His achievements remind us of the power of perseverance and intellectual curiosity.
1.3.5.1.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s commitment to the value of education over ignorance
Franklin said, “The only thing more expensive than education is ignorance.”
1.3.5.2 – How Benjamin Franklin’s vision shaped modern American identity
A Lasting Influence on American Identity Franklin’s vision for a society grounded in knowledge, civic engagement, and mutual support remains central to American identity. His contributions to the founding of the United States and his advocacy for education and personal responsibility continue to shape the nation’s values.

Benjamin Franklin’s signature as Postmaster serves as a powerful reminder of his vital contribution to colonial mail service and the foundation of early American communication. His influence helped shape the way information was disseminated, reflecting his enduring legacy in the development of postal systems.
1.4 – Franklin’s influence on Enlightenment thought and human nature
Discover how Benjamin Franklin shaped Enlightenment thought with his insights on human nature, reason, and progress, leaving a lasting impact on modern society.
Benjamin Franklin, a polymath whose contributions spanned many fields, left a lasting impact through his philosophy. Rooted in Enlightenment ideals, his thinking emphasized reason, personal improvement, and social responsibility. Franklin’s insights into human nature, education, and civic duty offer timeless lessons.
1.4.1 – How Benjamin Franklin’s ideas shaped modern philosophy
Franklin’s ideas were shaped by the Enlightenment’s focus on reason, scientific inquiry, and individual liberty. He believed in humanity’s potential for growth through education and experience.
1.4.1.1 – How Franklin emphasized reason in personal and public life
Franklin championed reason as a guiding principle in personal and public life. He advocated for empirical evidence over superstition, evident in his scientific work. His belief in reason was succinctly captured in his quote, “The way to see by faith is to shut the eye of reason.”
1.4.1.2 – How Benjamin Franklin promoted accessible education in America
Franklin believed in lifelong learning and its transformative power. He founded the Library Company of Philadelphia and helped establish the University of Pennsylvania, reflecting his commitment to accessible education. He famously said, “An investment in knowledge pays the best interest,” embodying his lifelong pursuit of learning through reading, experimentation, and dialogue.
1.4.2 – How Franklin understood self-interest and human potential
Franklin’s understanding of human nature balanced optimism and realism, acknowledging self-interest while recognizing human potential for altruism.
1.4.2.1 – How Benjamin Franklin balanced self-interest with civic good
While Franklin understood that self-interest drives human behavior, he believed that personal interests could align with the greater good. His quote, “No man is an island, entire of itself; every man is a piece of the continent,” reflects his belief in interconnectedness and the importance of community. He encouraged civic engagement and volunteerism as means of contributing to society.
1.4.2.2 – The role of virtue in Benjamin Franklin’s personal and societal views
Franklin emphasized the cultivation of virtue, including temperance, silence, and humility. He developed a system of thirteen virtues and tracked his adherence to them, believing that virtue was key to personal growth and societal harmony. His quote, “It is easier to suppress the first desire than to satisfy all that follow it,” underscores the importance of self-control.
1.4.3 – How Benjamin Franklin promoted philanthropy and civic responsibility
Franklin extended his philosophy beyond personal development to include civic responsibility and community engagement.
1.4.3.1 – How Franklin’s philanthropy shaped American society
Franklin’s life exemplified public service and philanthropy. He founded organizations like the first volunteer fire department in Philadelphia and the Pennsylvania Hospital. His belief that “Doing well by doing good” encapsulated his view that personal success should be linked to social responsibility. Franklin knew that vibrant communities depended on active participation.
1.4.3.2 – How Benjamin Franklin believed in the power of dialogue for democracy
Franklin valued open discourse and debate as essential for a healthy democracy. His involvement in the Junto, a club for mutual improvement, demonstrated his commitment to intellectual engagement. His quote, “Without continual growth and progress, such words as improvement, achievement, and success have no meaning,” reflects his belief that societies evolve through critical thinking and shared ideas.
1.4.4 – How Franklin shaped American values through Enlightenment principles
Franklin’s ideas have profoundly shaped American culture, particularly his emphasis on reason, education, and civic responsibility.
1.4.4.1 – How Franklin’s ideas on success reflect the American Dream
Franklin promoted the idea that success is achievable through hard work and perseverance. His rise from modest beginnings to statesman and scientist embodies this concept. His quote, “The Constitution only gives people the right to pursue happiness. You have to catch it yourself,” encourages individuals to actively seek their goals.
1.4.4.2 – How Franklin’s Enlightenment ideals continue to influence America
Franklin’s commitment to Enlightenment principles of reason, skepticism, and the pursuit of knowledge continues to influence American thought. His writings stress the importance of critical thinking and an informed citizenry in democracy. His quote, “We are all born ignorant, but one must work hard to remain stupid,” encourages ongoing learning and questioning of assumptions.
1.4.5 – How Franklin’s humor offered insights into human nature
Franklin’s wit and humor offered profound insights into human nature, often conveyed through his proverbs and sayings.
1.4.5.1 – How Benjamin Franklin’s proverbs offer practical life advice
Franklin’s proverbs, such as “A penny saved is a penny earned,” offer timeless advice on frugality and prudence. His practical approach to life and sharp observations of human behavior make his philosophy relevant across generations.
1.4.5.2 – How Benjamin Franklin’s life stories reflect his moral philosophy
Many anecdotes from Franklin’s life illustrate his philosophical beliefs. His commitment to humility, self-improvement, and learning from others shows his dedication to personal growth. His willingness to admit mistakes and embrace criticism highlights the value of humility in life.
1.5 – How Benjamin Franklin shaped American values and society
Discover how Benjamin Franklin shaped American values and society through his innovations, leadership, and ideals, leaving a lasting impact on the nation’s identity.
Benjamin Franklin is a key figure in American history, not only for his direct contributions to the founding of the United States but also for the lasting influence of his ideas. His impact spans education, civic responsibility, and social reform, making him a subject of great interest to educators, historians, and the public. Franklin’s legacy touches many aspects of society, culture, and governance, and his principles continue to resonate in modern life.
Understanding Franklin’s cultural impact requires examining how his ideas have shaped American values. He was not just a Founding Father, but a cultural icon whose thoughts on freedom, knowledge, and community service have inspired generations. This exploration will delve into Franklin’s influence on American culture, his contributions to education and civic engagement, and how his principles continue to influence society today.
1.5.1 – How Benjamin Franklin became a symbol of American ingenuity
Franklin’s persona has evolved into a symbol of American ingenuity and independence. His legacy is reflected in cultural artifacts, literature, and popular media, where he is often portrayed as the epitome of American ideals.
1.5.1.1 – How Benjamin Franklin’s image represents American ideals
Franklin’s image has been widely spread through portraits, currency, and public monuments. His likeness on the $100 bill symbolizes American values like hard work, thrift, and intellectual achievement. The phrase “A penny saved is a penny earned” continues to reflect his ethos of frugality and self-reliance.
1.5.1.2 – How Benjamin Franklin is portrayed in popular culture
Franklin’s influence extends into literature and film, where he is often depicted as a wise elder or inventor. His autobiography remains a classic of American literature, offering insights into his life and philosophy. In popular culture, Franklin appears in films and television shows, reinforcing his status as a cultural icon.
1.5.1.2.1 – Educational quotes from Benjamin Franklin that inspire modern learning
“An investment in knowledge pays the best interest” remains relevant in discussions about education and self-improvement.
1.5.2 – Franklin’s commitment to education and public libraries
One of Franklin’s most enduring legacies is his commitment to education and the promotion of knowledge. He believed that education was foundational to a democratic society and should be accessible to all.
1.5.2.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s role in founding the University of Pennsylvania
Franklin founded several educational institutions, notably the University of Pennsylvania, which was the first to offer a curriculum blending practical and liberal arts. His vision was to create an institution that fostered intellectual curiosity and practical skills, encouraging students to engage with the world.
1.5.2.1.1 – Franklin’s approach to teaching and the importance of active learning
The saying, “Tell me, and I may forget. Teach me, and I might recall. Engage me, and I truly learn,” highlights the importance of hands-on learning experiences.
1.5.2.2 – How Benjamin Franklin promoted public libraries for education
Franklin recognized the importance of accessible knowledge for the public. He founded the Library Company of Philadelphia, the first subscription library in America, making books available to those who could not afford them. Franklin believed that an informed citizenry was crucial to democracy.
1.5.2.2.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s view on learning through mistakes and knowledge
“There is no harm in being sometimes wrong — especially if one is promptly found out,” reflects his belief in the value of knowledge and the acceptance of error as part of learning.
1.5.3 – How Benjamin Franklin advocated for social responsibility and progress
Franklin’s commitment to civic engagement and social responsibility is another significant part of his legacy. He believed that individuals had a duty to contribute to their communities and work toward the common good.
1.5.3.1 – How Benjamin Franklin helped create Philadelphia’s first volunteer fire department
Franklin helped establish numerous civic organizations, including the first volunteer fire department in Philadelphia and the Pennsylvania Hospital. These initiatives demonstrated his belief that active participation in community service was key to societal improvement.
1.5.3.1.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s call for unity in social and civic matters
“We must, indeed, all hang together or, most assuredly, we shall all hang separately,” highlights the importance of unity in addressing social challenges.
1.5.3.2 – How Franklin’s advocacy for social justice shaped America
Franklin was ahead of his time in supporting social reforms such as the abolition of slavery, women’s education, and public health initiatives. His efforts reflected his belief that progress required the active involvement of all members of society.
1.5.3.2.1 – Justice and equality in Franklin’s vision for America
“Justice will not be served until those who are unaffected are as outraged as those who are,” underscores his commitment to social equity and justice.
1.5.4 – How Franklin’s Enlightenment values shaped American philosophy
Franklin’s philosophical contributions continue to influence contemporary discussions about personal responsibility, civic duty, and the pursuit of knowledge. His principles are reflected in various aspects of American life, from education to governance.
1.5.4.1 – The self-made man ethos in Benjamin Franklin’s life and legacy
Franklin is often associated with the idea of the American Dream — the belief that anyone can achieve success through hard work and determination. His life story, from a poor boy in Boston to a renowned statesman and inventor, serves as an inspiration.
1.5.4.1.1 – The pursuit of happiness according to Benjamin Franklin’s worldview
The Constitution grants individuals the freedom to seek happiness, but attaining it is a personal endeavor that requires effort and determination.
1.5.4.2 – The role of Benjamin Franklin in promoting Enlightenment principles
Franklin’s ideas were rooted in Enlightenment values, emphasizing reason, scientific inquiry, and the importance of knowledge. His contributions to science, particularly in electricity and meteorology, demonstrate his belief in human ingenuity.
1.5.4.2.1 – Franklin’s view on personal and societal growth as key to success
The phrase, “Without continual growth and progress, such words as improvement, achievement, and success have no meaning,” reminds us of the importance of innovation in society.
1.5.5 – Franklin’s influence on contemporary issues like education and civic duty
Franklin’s ideas remain relevant today. As issues like education reform, civic engagement, and social responsibility continue to be pressing topics, his insights offer valuable guidance.
1.5.5.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s emphasis on lifelong learning and education today
The emphasis on education as a means of empowerment remains powerful today. Franklin’s belief in lifelong learning encourages individuals to actively seek knowledge and engage with their communities.
1.5.5.1.1 – The enduring relevance of Benjamin Franklin’s views on education
“An educated mind is the best weapon,” highlights the importance of education in fostering critical thinking and informed citizenship.
1.5.5.2 – How Franklin’s legacy of civic service continues to inspire community involvement
In today’s world, Franklin’s legacy of community service is more important than ever. His encouragement for individuals to contribute to the common good serves as a call to action for modern citizens.
1.5.5.2.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s philosophy on service to others and personal growth
“The best way to find yourself is to lose yourself in the service of others” continues to inspire volunteerism and activism today.
1.6 – Surprising stories and inventions of Benjamin Franklin
Discover surprising stories and inventions of Benjamin Franklin, from bifocals to the lightning rod. Explore his genius and lesser-known contributions to history!
Benjamin Franklin celebrated as a Founding Father, inventor, and diplomat, led a life full of fascinating facts and lesser-known anecdotes. His multifaceted personality and intellect are revealed through these stories, offering insights into his character and the experiences that shaped his contributions to society.
This section highlights intriguing facts about Franklin, showcasing his wit, wisdom, and influence on American culture.
1.6.1 – How Benjamin Franklin’s youth shaped his intellectual journey
1.6.1.1 – How Franklin’s printing work influenced his future ideas
Franklin began his career in Boston in 1706 as a printer’s apprentice at age 12. He secretly published articles under a pseudonym, often criticizing his brother’s political views. This early rebellion showed his determination to voice his opinions and his commitment to learning, as reflected in his quote, “I am not ashamed to confess that I am ignorant of what I do not know.”
1.6.1.2 – The story behind Franklin’s “Water American” and temperance beliefs
The “Water American” Joke Known for his sharp wit, Franklin coined the term “water American” to describe Americans who preferred water over alcohol. This playful jab highlighted his belief in temperance and moderation, as seen in his writings such as Poor Richard’s Almanack, where humorous proverbs continue to resonate.
1.6.2 – How Benjamin Franklin’s creativity transformed daily life
1.6.2.1 – How Benjamin Franklin invented the Franklin stove for better heating
Franklin’s invention of the Franklin stove improved heating efficiency by providing better heat circulation and reducing smoke. This practical innovation reflected his belief in solving everyday problems, encapsulated by his quote, “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.”
1.6.2.2 – Innovations by Benjamin Franklin
Franklin also created bifocal glasses and the glass armonica, a musical instrument made of glass bowls. His inventive spirit valued both functionality and beauty, reflected in his quote, “The only thing more expensive than education is ignorance.”
1.6.3 – Surprising alliances forged by Benjamin Franklin in Europe
1.6.3.1 – Franklin as America’s ambassador to France
As a diplomat during the American Revolution, Franklin’s charm and intellect earned the respect of the French court. His quote, “In this world, nothing can be said to be certain, except death and taxes,” humorously captures his understanding of diplomacy and human nature.
1.6.3.2 – Franklin’s influence on European intellectuals during his time in France
Cultural Exchange In France, Franklin bridged American and European intellectuals by hosting salons where Enlightenment thinkers gathered. His simple attire and wit challenged societal norms, highlighting his ability to engage with high society while promoting American ideals.
1.6.4 – How Franklin’s philanthropy transformed American society
1.6.4.1 – How Franklin’s Library Company made books accessible to the public
In 1731, Franklin founded the Library Company of Philadelphia, the first subscription library in America, making books accessible to the public. His belief in education is reflected in his quote, “An investment in knowledge pays the best interest.”
1.6.4.2 – How Franklin improved healthcare with the Pennsylvania Hospital
Franklin co-founded the Pennsylvania Hospital in 1751, emphasizing healthcare and social welfare. His commitment to improving society is reflected in his belief that “A good example is the best sermon.”
1.6.5 – The personal life and unique habits of Benjamin Franklin
1.6.5.1 – How Franklin used chess to promote strategic thinking
Franklin was an avid chess player, using the game to relax and exercise his mind. In his essay “The Morals of Chess,” he compared the game to life, emphasizing strategy and foresight.
1.6.5.2 – How Franklin’s unique sleep schedule enhanced his efficiency
Franklin adopted a unique sleep schedule, waking up early and going to bed early to maximize productivity. His famous motto, “Early to bed and early to rise makes a man healthy, wealthy, and wise,” has become ingrained in American culture.
1.6.6 – How Franklin used humor to address serious societal issues
1.6.6.1 – Benjamin Franklin’s famous proverbs
Franklin was known for his memorable proverbs, such as “A stitch in time saves nine” and “God helps those who help themselves.” His ability to distill complex ideas into simple phrases made him a beloved figure in American folklore.
1.6.6.2 – The funniest stories about Benjamin Franklin’s political wit
Franklin’s wit also shone in his humorous anecdotes. One notable story recounts his suggestion that the British government should tax its own citizens to pay for their military expenses in America, humorously advising them to “keep the kettle boiling” while they figured out their fiscal problems.
1.6.7 – Franklin’s enduring role as a symbol of American values
1.6.7.1 – How Benjamin Franklin’s ideas influence today’s social systems
Franklin’s impact on American society endures. His emphasis on education, civic duty, and social responsibility continues to resonate today, serving as a model of intellectual curiosity and community engagement.
1.6.7.2 – How Franklin’s image became iconic in U.S. history
Franklin’s image and sayings are deeply ingrained in American culture, and frequently referenced in discussions about values, success, and personal development. His life remains a testament to perseverance and the pursuit of knowledge.
1.7 – Lifelong Lessons from Benjamin Franklin’s Achievements
Discover valuable lifelong lessons from Benjamin Franklin’s achievements, exploring his wisdom, innovations, and principles that shaped American history and success.
Exploring the life and legacy of Benjamin Franklin reveals a multifaceted individual whose contributions have deeply influenced American society. As a Founding Father, Franklin’s ideas on democracy, science, and civic responsibility continue to resonate. His inventions and discoveries enhanced 18th-century life and laid the foundation for future innovations. In today’s digital age, Franklin’s impact serves as a reminder to embrace curiosity and lifelong learning. By studying his achievements and philosophies, we not only honor his legacy but also gain insights that promote civic engagement and intellectual growth. Franklin’s journey reminds us that knowledge is a powerful tool that can shape our future, just as it did for him and the nation he helped to build.
1.8 – How to Learn More About Benjamin Franklin’s Contributions
Discover the key contributions of Benjamin Franklin and explore resources to learn more about his impact on science, politics, and innovation in U.S. history.
Continue exploring the remarkable life of Benjamin Franklin. His dedication to knowledge, innovation, and civic duty underscores the profound impact one individual can have on society. If this information resonates with you, seek more resources on Franklin’s philosophies, inventions, and contributions to American history. Engage with books, documentaries, and online courses to deepen your understanding. Participate in discussions to share what you’ve learned and encourage others to appreciate history. By fostering curiosity, you contribute to a more informed society, just as Franklin advocated.