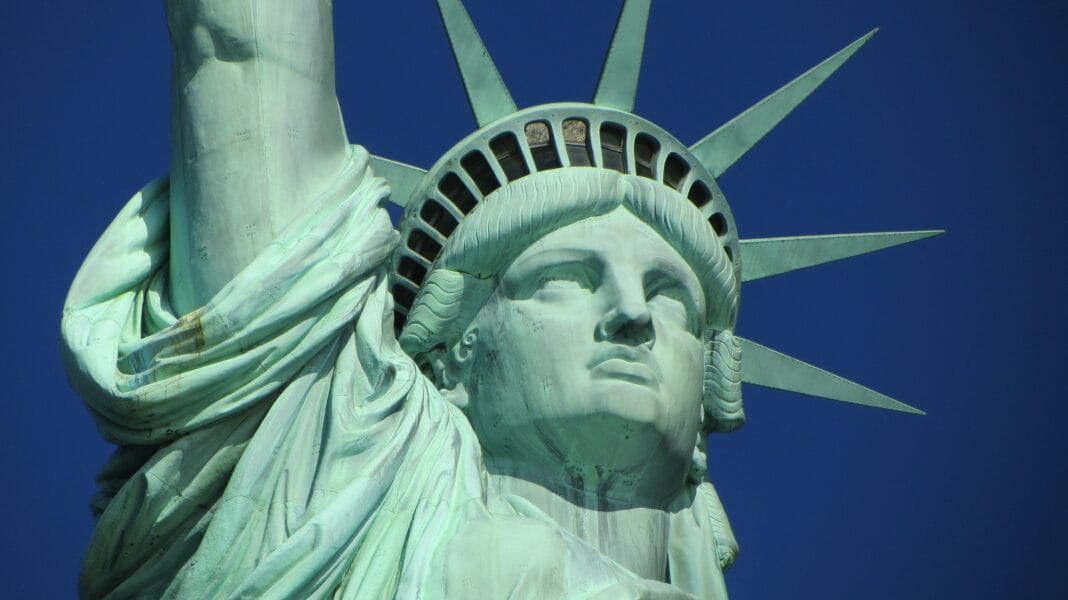
Liberty
Explore the essence of Liberty—its history, impact, and significance in shaping democracy and individual rights. A deep dive into freedom’s true meaning.
1.2 – Exploring Liberty Through Quotes and Insights on Compassion and Ethics
Discover thought-provoking quotes and insights on liberty, compassion, and ethics. Explore how freedom connects with moral values in shaping a just society.
Humanity encompasses values, beliefs, and actions that define the human experience. At its core, it involves compassion, ethics, and our drive to improve the lives of others—a pursuit seen throughout history, philosophy, and religion.
Figures like Mahatma Gandhi and Mother Teresa dedicated their lives to promoting kindness and understanding. Gandhi’s quote, “The best way to find yourself is to lose yourself in the service of others,” illustrates how self-discovery is often linked with compassion. Today, humanity’s role is more crucial than ever as we address issues such as inequality, environmental challenges, and the impact of technology on human connections. Many seek ways to lead more compassionate lives, support humanitarian causes, and contribute to a better society.
As the world becomes increasingly connected, humanitarian stories from around the globe—ranging from community-building projects to transformative charitable efforts—continue to inspire. Resources that highlight how values like kindness and respect contribute to personal success and community welfare resonate with audiences.
For further exploration of the ethics of humanity, compassion in practice, and fostering empathy, check the highlighted links throughout the blog for deeper insights into living with compassion and purpose.
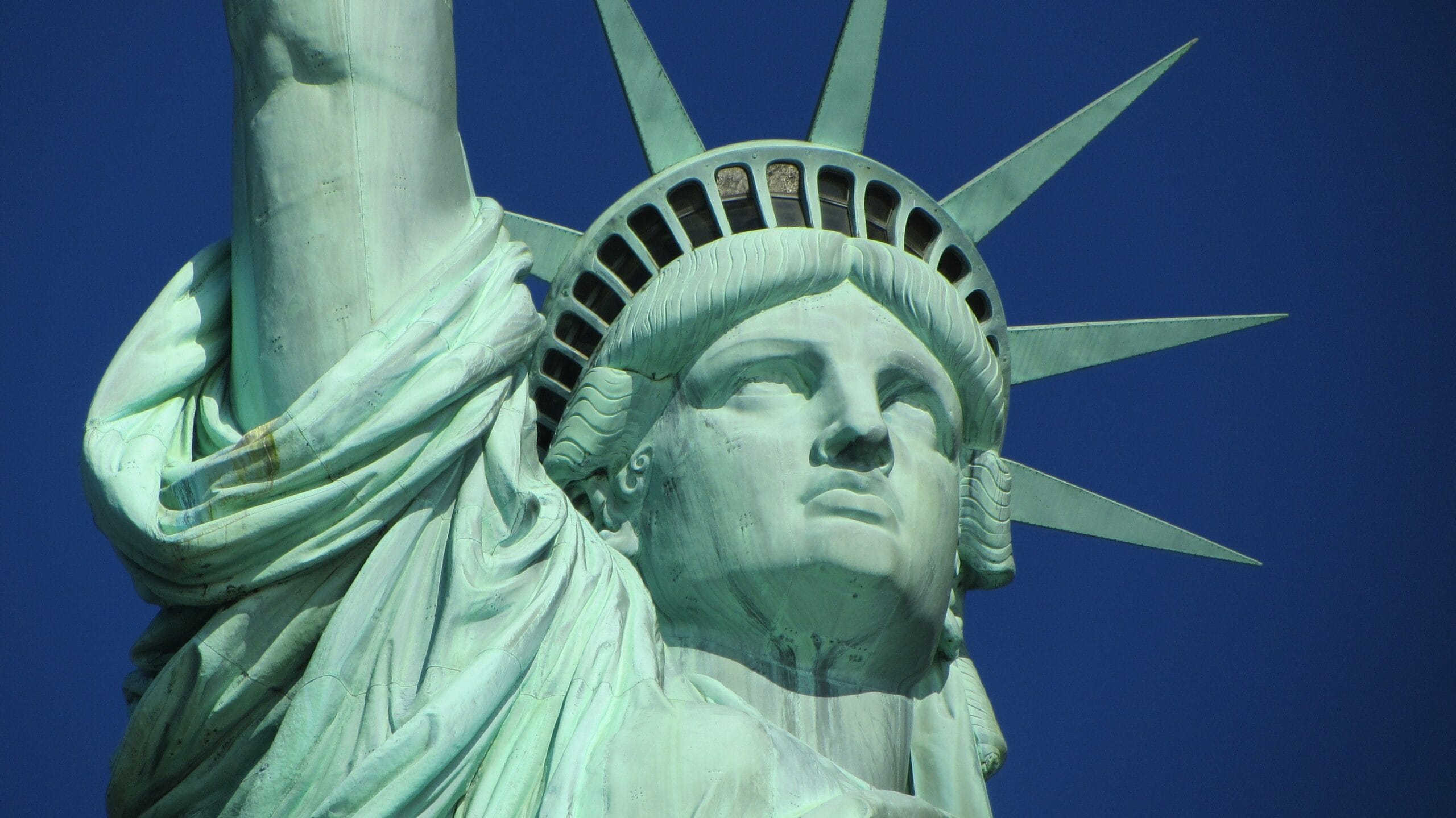

1.3 – How Liberty Shapes the Concept of Humanity
Discover how liberty influences human identity, values, and society, shaping our understanding of freedom, rights, and what it means to be truly human.
Humanity encompasses values, ethics, compassion, and the ways we connect with others. It’s about both personal growth and contributing to the collective good, which can be seen in acts of kindness, standing up for justice, or simple compassionate gestures.
At its core, humanity involves empathy—the ability to understand another’s perspective. As Maya Angelou said, “I think a hero is any person really intent on making this a better place for all people.” This highlights how individuals can contribute to a better society through empathy and kindness.
1.3.1 – How Liberty Drives the Fundamental Elements of Humanity
1.3.1.1 – How Compassion and Liberty Work Together for Humanity
- Compassion is a core trait that defines humanity, motivating individuals to alleviate others’ suffering. It has inspired humanitarian movements throughout history. Muhammad Ali’s famous quote, “Service to others is the rent you pay for your room here on Earth,” shows how impactful compassionate service can be.
- Acts of compassion vary from volunteering to advocating for justice in underrepresented communities. Stories like Clara Barton’s work founding the American Red Cross inspire by showing the lasting impact of compassion.
1.3.1.2 – Liberty as a Foundation for Human Ethics and Responsibility
- Humanity is closely linked to ethics and responsibility. Ethical behavior includes respect, fairness, and integrity, guiding individuals to act for the collective good. Albert Schweitzer said, “Ethics is the activity of man directed to secure the inner perfection of his own personality.” This foundation gives meaning to actions and decisions.
- Ethical choices extend to global issues such as environmental preservation, economic justice, and community welfare. Many seek practical steps to apply these values, like reducing waste or supporting fair policies.
1.3.1.3 – How Liberty Supports Human Rights and Equality in Society
- Human rights are a fundamental aspect of humanity, ensuring that everyone’s dignity is respected. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) states, “All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights.” This principle resonates deeply, particularly in societies where individual rights are foundational.
- Fighting for human rights takes many forms, from supporting legislative changes to combating discrimination. Figures like Martin Luther King Jr., who fought for civil rights, serve as enduring symbols of the power of equality and justice.
1.3.1.4 – How Liberty Promotes Empathy in a Divided World
- Empathy lies at the heart of human connection. It involves stepping into another person’s perspective and striving to grasp their feelings and needs. As Brené Brown insightfully expressed, empathy isn’t a rigid process with set rules—it’s about actively listening, offering support, suspending judgment, forging emotional bonds, and conveying the reassuring message: “You’re not alone.”
- Empathy is key in personal and professional relationships. Readers often seek advice on developing empathy, such as active listening, volunteering, or practicing patience.
1.3.1.5 – How Liberty Inspires Daily Acts of Kindness and Compassion
- Kindness is a simple, accessible form of humanity that creates a ripple effect in communities. Princess Diana’s words, “Carry out a random act of kindness, with no expectation of reward,” emphasize its far-reaching impact.
- In today’s fast-paced world, many seek ways to integrate kindness into daily life, from small acts of courtesy to supporting local initiatives or helping neighbors in need.
1.3.1.6 – How Liberty Drives Humanitarian Innovation in Technology
- Technology impacts human connection and raises ethical concerns. Digital advancements enable global interactions but also pose challenges regarding privacy, mental health, and social impact. Readers are often interested in how technology can be used to foster empathy and drive positive change.
- Innovations like online mental health support and community aid platforms demonstrate how technology can be leveraged for humanitarian purposes.
1.3.2 – Historical Quotes Reflecting Liberty and Human Compassion
1.3.2.1 – Liberty and Humanity in Mahatma Gandhi’s Teachings
“The greatness of humanity is not in being human, but in being humane.” – Mahatma Gandhi. This quote emphasizes that true greatness lies in compassion and kindness.
1.3.2.2 – Anne Frank’s Wisdom on Liberty and Generosity
“No one has ever become poor by giving.” – Anne Frank. This universal truth reflects the joy in generosity and philanthropy.
1.3.2.3 – Harriet Tubman’s Role in Liberty and Human Rights
Harriet Tubman’s leadership in helping enslaved people to freedom is a testament to the courage and determination that underpin humanity. Her legacy continues to inspire those committed to justice and human rights.
1.3.2.4 – Albert Pine on Liberty and Humanity
“What we do for ourselves dies with us. What we do for others and the world remains and is immortal.” – Albert Pine. This statement reinforces the idea that our actions for others define our legacy.
1.3.3 – How Liberty Shapes Our Final Thoughts on Human Connection and Equality
Understanding humanity involves recognizing key qualities—compassion, ethics, empathy, and kindness—that bind us together. These values shape our decisions, strengthen communities, and drive social progress. By drawing inspiration from figures and everyday examples, we can gain insights into how to contribute to a more humane society. Whether through acts of kindness, standing up for human rights, or simply listening with empathy, humanity remains as relevant today as ever.
To explore ethical behavior, human rights initiatives, and acts of kindness, check the highlighted anchor texts throughout the blog.

In 1915, the PWSA released a powerful image of the Liberty Bell, a profound symbol of liberty and justice. This iconic landmark stands as a testament to America’s unwavering commitment to freedom, conveying a timeless message that resonates deeply throughout our nation’s history.
1.4 – How humanity and compassion shape societies
Discover how humanity and compassion influence liberty, shaping societies through empathy, justice, and collective progress in an ever-evolving world.
Humanity and compassion are powerful forces that shape societies worldwide. Understanding these concepts goes beyond kindness; it’s about actively dedicating oneself to making a positive impact on others’ lives. This article delves into the role of compassion in history, its ongoing influence, and how it continues to foster social change.
With a growing interest in community service, social justice, and ethical practices, many are seeking ways to live compassionately. People look to figures like Martin Luther King Jr., Mother Teresa, and Malala Yousafzai for inspiration, as well as guidance on integrating empathy into their own lives. This article covers compassion in times of crisis, the role of community initiatives, and how small, consistent acts of kindness can benefit individual well-being and society.
1.4.1 – Liberty and Historical Figures Who Championed Empathy
1.4.1.1 – Compassionate leadership lessons from historical figures
- Throughout history, leaders have demonstrated the transformative power of compassion. Figures like Mahatma Gandhi, Nelson Mandela, and Eleanor Roosevelt championed humanitarian causes with empathy, equality, and non-violence. Gandhi’s quote, “The best way to find yourself is to lose yourself in the service of others,” encapsulates how selflessness can lead to meaningful change.
- These leaders showed how compassion, combined with purpose and courage, can challenge injustice and inspire generations to prioritize human welfare over personal gain.
1.4.1.2 – How Compassionate Movements Spark Social Change
- Compassionate action has driven numerous social movements. In the U.S., the civil rights movement, women’s suffrage, and anti-war efforts were sparked by empathy for marginalized groups. Martin Luther King Jr.’s famous words, “Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere,” highlight how compassion can inspire people to fight for justice.
- These movements remind us of the value of collective compassion and its lasting impact on society.
1.4.2 – How Community Initiatives Create Lasting Change
1.4.2.1 – How local organizations drive global change through compassion
- Compassion often begins at the community level. Local organizations, churches, and nonprofits address poverty, education gaps, and health disparities. Initiatives like Habitat for Humanity, the American Red Cross, and the Make-A-Wish Foundation turn compassion into tangible support for thousands of people.
- On a global scale, organizations like UNICEF and Doctors Without Borders provide vital resources and relief to those affected by conflict, natural disasters, and poverty, demonstrating how compassion can create lasting solutions to world challenges.
1.4.2.2 – How compassion helps communities in times of crisis
- Crises often reveal humanity’s deepest compassion. After natural disasters or health emergencies, communities come together to provide shelter, food, and aid. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, countless acts of kindness emerged—from healthcare workers putting their lives at risk to volunteers distributing meals.
- These moments of unity and empathy remind us of the importance of compassion, both locally and globally, during times of need.
1.4.3 – Liberty and the value of everyday compassionate actions
1.4.3.1 – How everyday kindness contributes to societal well-being
- Small acts of kindness, like holding the door for a stranger or offering a listening ear, can have a significant impact. These simple gestures help build a sense of community and can brighten someone’s day. As Princess Diana said, “Carry out a random act of kindness, with no expectation of reward, safe in the knowledge that one day someone might do the same for you.”
- By starting with small gestures, individuals can create a ripple effect that strengthens connections within families, neighborhoods, and workplaces.
1.4.3.2 – Liberty and volunteerism as a path to social change
- Volunteering is a powerful way to show compassion. Whether helping at a food bank or tutoring underprivileged children, volunteer efforts reflect a commitment to supporting others. Volunteering not only benefits those in need but also provides a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
- Many seek volunteer opportunities that align with their skills and interests. Engaging in these activities promotes personal growth and contributes positively to society.
1.4.4 – Liberty and media
1.4.4.1 – Liberty and media’s power to highlight compassionate actions
- Media plays a key role in shaping perspectives on compassion. Uplifting stories of heroism, resilience, and kindness inspire hope and resonate with audiences. Documentaries, news stories, and social media campaigns highlighting humanitarian efforts foster positive narratives in a challenging world.
- Platforms like GoFundMe and YouTube allow people to connect with causes they care about, reinforcing the idea that compassion can be collective and far-reaching.
1.4.4.2 – How stories create a deeper understanding of compassion
- Storytelling helps us see the world from others’ perspectives, fostering empathy. This approach, found in journalism, literature, and film, can evoke a strong sense of understanding for others’ experiences. Books like To Kill a Mockingbird and The Diary of Anne Frank offer powerful insights into human struggles, encouraging readers to reflect on their own beliefs and actions.
1.4.5 – Liberty and the role of compassion in personal fulfillment
1.4.5.1 – Liberty and the health benefits of compassionate living
- Research shows that compassion positively impacts both mental and physical health. Acts of kindness release feel-good hormones like oxytocin and serotonin, improving mood and reducing stress. Studies indicate that people who engage in compassionate acts are happier and have a greater sense of purpose.
- Understanding the health benefits of compassion can motivate individuals to adopt a more empathetic mindset.
1.4.5.2 – Liberty and compassion-driven educational and workplace cultures
- Compassionate schools and workplaces foster supportive environments. Programs that focus on emotional intelligence, empathy, and kindness help students and employees develop strong social skills. Compassionate workplaces lead to higher job satisfaction, stronger morale, and better productivity.
- Practical steps like active listening, recognizing achievements, and practicing patience help build trust and create a positive environment in professional settings.
1.4.6 – Liberty and the inspiring words of compassionate leaders
1.4.6.1 – How Anne Frank’s words inspire acts of kindness
“Wherever there is a human being, there is an opportunity for kindness.” – Seneca
1.4.6.2 – Seneca’s wisdom on kindness and its transformative power
The story of Mother Teresa’s work in Calcutta illustrates the power of selfless compassion. Despite facing challenges, she dedicated her life to helping the poor, embodying how compassion uplifts communities.
1.4.6.3 – How Leo Buscaglia’s words inspire small acts of kindness
“Too often we underestimate the power of a touch, a smile, a kind word, a listening ear…” – Leo Buscaglia
1.4.7 – How compassion continues to inspire positive change
Compassion is a fundamental aspect of humanity, influencing individuals and societies alike. Reflecting on historical examples, everyday kindness, volunteerism, and the impact of compassionate media demonstrates how empathy can heal, unite, and inspire. These insights offer valuable guidance for creating a positive impact in both personal and communal life.
To learn more about compassionate volunteer opportunities, inspiring historical figures, and simple acts of kindness, check the highlighted anchor texts throughout the blog.

Ground-level view of the Statue of Liberty and oblique aerial views of Ellis Island, highlighting its history, ferry routes, and key landmarks.
1.5 – Liberty and moral principles in human history
Explore how liberty has shaped moral principles throughout human history, influencing societies, governance, and individual rights in the pursuit of freedom.
The ethical foundations of humanity form the moral backbone of societies, influencing laws, behaviors, and collective values. Understanding these principles sheds light on how deeply held beliefs shape culture, governance, and interpersonal relationships. Ethics often inspire personal reflection and community action, prompting questions like: What does it mean to live a moral life? How can I make ethical choices in my daily life?
This section explores the essence of humanity’s ethical foundations, including justice, empathy, and equality across history and philosophy. We’ll examine the thoughts of philosophers like Immanuel Kant, religious and secular traditions, and cultural milestones that shaped modern ethical ideals. We’ll also highlight quotes, anecdotes, and practical examples to bring these ideas to life.
1.5.1 – How Liberty Shaped Historical Ethical Foundations
1.5.1.1 – How ancient cultures defined liberty and justice
- Humanity’s ethical principles have roots in early civilizations, where ideas of justice and reciprocity became formalized. Ancient Egypt’s Ma’at, symbolizing truth, balance, and justice, encouraged citizens to live harmoniously.
- Similarly, ancient Mesopotamian laws, like the Code of Hammurabi, promoted social justice by setting rules for fair treatment. The principle of “an eye for an eye” symbolized justice within their cultural framework, emphasizing consequences for harmful actions.
- Greek philosophers such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle established ideas on virtue and moral responsibility that continue to shape Western ethical thought. Aristotle’s Nicomachean Ethics emphasized a “virtuous mean” — a balanced life of moderation, courage, and kindness, which remains influential today.
1.5.1.2 – How religion influenced the ethical concept of liberty
- Many find guidance in religious teachings. Christianity’s Golden Rule—“Do unto others as you would have them do unto you”—captures the essence of ethical reciprocity, an idea central to various faiths.
- Buddhism emphasizes compassion and non-violence, encouraging adherents to reduce suffering, an idea popularized by figures like the Dalai Lama. Judaism also has principles rooted in justice, charity, and ethical treatment of others, promoting universal kindness and empathy.
- Islam’s emphasis on community welfare highlights ethical altruism. These teachings across religions underscore shared values of love, respect, and humanity that continue to inspire people worldwide.
1.5.2 – Philosophical insights on liberty and ethical humanity
1.5.2.1 – How Kantian ethics supports the concept of liberty
- Immanuel Kant’s categorical imperative argues that people should act in ways they would want universally applied. This principle shapes duty-based ethics, suggesting actions should be judged by adherence to moral laws, not consequences.
- Kant’s ideas promote a sense of duty towards others and emphasize treating individuals as ends in themselves, not as means to an end. This remains central to discussions on human rights and dignity.
1.5.2.2 – How utilitarianism balances liberty and the greater good
- Philosopher John Stuart Mill’s utilitarianism stresses that ethical actions are those creating the greatest happiness for the greatest number. This principle encourages individuals to weigh consequences, prioritizing outcomes that foster well-being.
- Utilitarianism provides a practical approach to ethics, especially relevant in policy decisions, law, and business practices. It encourages people to consider the broader impact of their actions on society.
1.5.3 – How liberty underpins the ethical pursuit of equality
1.5.3.1 – How liberty drives ethical equality in society
- Social justice is a powerful ethical issue, with roots in movements like the civil rights struggle for equality, fairness, and dignity. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. championed equality, stating, “Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere.” His words emphasize the ethical need to eliminate inequalities.
- Today, social justice continues to shape discussions on race, gender, and economic inequality, providing an ethical framework for creating fair policies and fostering a more equal world.
1.5.3.2 – How liberty supports ethical human rights principles
- The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted in 1948, embodies global ethical principles, emphasizing the inherent dignity and worth of every person. This document serves as a universal moral compass, reminding us that all humans deserve respect, safety, and freedom.
- Human rights principles drive legal protections, from anti-discrimination laws to labor rights. Studying these principles provides insight into the ethical foundations that protect individual freedoms and societal well-being.
1.5.4 – How liberty promotes empathy in ethical decision-making
1.5.4.1 – How empathy enhances the concept of liberty in ethics
- Empathy, the ability to understand and share others’ feelings, forms the heart of ethical humanity. Philosopher David Hume noted, “The greatest of all virtues is humanity.” His words highlight the importance of compassion in ethical decisions.
- Empathy encourages selfless actions and support for others. Understanding empathy as an ethical foundation can guide compassionate actions in personal and professional contexts.
1.5.4.2 – How liberty encourages altruism in society
- Altruism—acting for the benefit of others—is another essential part of ethical humanity. Historical figures like Mother Teresa exemplified altruism, dedicating their lives to helping those in need. Her legacy continues to inspire charitable work and compassionate outreach.
- Ethical altruism aligns with values of kindness and community, offering practical ways for individuals to contribute to causes and make meaningful contributions.
1.5.5 – How liberty influences ethical decision-making in today’s world
1.5.5.1 – How liberty impacts ethics in modern business practices
- With rapid technological advancements, ethical issues arise, particularly around data privacy, artificial intelligence, and environmental impact. Businesses are encouraged to adopt ethical practices that prioritize transparency and consumer welfare.
- Understanding these ethical challenges is crucial as ethical frameworks help individuals and companies navigate decisions while considering broader social impacts.
1.5.5.2 – How Liberty Shapes Ethical Environmental Decisions
- With growing awareness of climate change, environmental ethics has become central to discussions on sustainability. Ethical humanity requires accountability for how actions affect the planet, emphasizing responsibility to future generations.
- Ethical guidance often calls for minimizing consumption, promoting conservation, and supporting eco-friendly policies—practical steps individuals can take to protect the Earth.
1.5.6 – Quotes on liberty and ethical humanity
1.5.6.1 – Potter Stewart’s view on liberty and ethics
“Ethics is knowing the difference between what you have a right to do and what is right to do.” – Potter Stewart. This highlights the importance of moral choices beyond legality.
1.5.6.2 – How Desmond Tutu’s quote emphasizes liberty and justice
“I am not interested in picking up crumbs of compassion thrown from the table of someone who considers himself my master. I want the full menu of rights.” – Desmond Tutu. His words remind us that true ethics involves equal respect and dignity for all.
1.5.6.3 – How Schweitzer’s philosophy relates to liberty and ethical humanity
Albert Schweitzer’s life and philosophy exemplify “reverence for life,” teaching that all living beings deserve compassion. His legacy promotes respect across species, reflecting ethical breadth.
1.5.6.4 – G.K. Chesterton on liberty and mutual responsibility
“We are all in the same boat, in a stormy sea, and we owe each other a terrible loyalty.” – G.K. Chesterton. This quote resonates with ethical discussions on mutual support and solidarity.
1.6 – How liberty connects humanity in global religions
Discover how liberty serves as a unifying force across global religions, shaping beliefs, values, and human connections in diverse faith traditions worldwide.
The concept of humanity transcends cultural and religious boundaries, embodying shared values like compassion, empathy, and mutual respect that have shaped civilizations throughout history. This exploration reveals how different societies understand and practice kindness, tolerance, and communal responsibility. As multicultural understanding becomes increasingly essential, this topic resonates with those curious about ethical commonalities and diverse perspectives that promote a more inclusive world.
From ancient civilizations to modern teachings, humanity is a thread woven through many cultures and religions. This section uncovers how major religions, indigenous beliefs, and philosophies embody and promote humanitarian values. Through historical quotes and relatable wisdom, we offer guidance for daily interactions and decision-making.
1.6.1 – The concept of liberty in major world religions
1.6.1.1 – How liberty shapes humanity in Christian values
- Christianity emphasizes agape (selfless love) as central to its teachings. The command to “love thy neighbor as thyself” calls for compassion and forgiveness, urging followers to extend kindness to all people. Jesus Christ’s teachings focused on mercy, charity, and love for mankind, particularly for the vulnerable.
- Mother Teresa’s life of service exemplifies humanity in Christianity. She famously said, “If you judge people, you have no time to love them,” highlighting the Christian ideal of embracing humanity without prejudice.
1.6.1.2 – Exploring liberty through the lens of Buddhist compassion
- Buddhism places karuna (compassion) at its core, encouraging followers to alleviate suffering for all beings. The Buddha taught that understanding and empathy are essential to breaking free from suffering.
- The Dalai Lama often emphasizes this principle, saying, “Our prime purpose in this life is to help others. And if you can’t help them, at least don’t hurt them.” His words guide the practice of humanity in both thought and action.
1.6.1.3 – How liberty fosters justice in Jewish traditions
- Judaism teaches tikkun olam, the duty to repair and improve the world. From the Torah’s commandments to love one’s neighbor, to ethical principles in the Talmud, Jewish teachings promote a proactive approach to making the world more compassionate and just.
- Jewish philosopher Maimonides said, “The purpose of all wisdom is to enable a person to perform what is just and right.” This reflects the belief that education and ethics serve to uplift humanity and aid those in need.
1.6.1.4 – How liberty promotes unity in Islamic teachings
- Islam emphasizes ummah, the global community, promoting unity and support among all people. Zakat (charitable giving) is one of Islam’s Five Pillars, emphasizing social responsibility and helping those in need.
- Prophet Muhammad’s teachings illustrate compassion, as in his saying, “The best among you are those who bring the greatest benefits to others.” This call for kindness defines the concept of humanity in Islam, encouraging generosity and fostering communal harmony.
1.6.1.5 – Hinduism’s message of liberty and non-violence
- In Hinduism, ahimsa represents non-violence and respect for all living beings. This principle is central to the faith, teaching adherents to treat others with empathy and avoid harm in thoughts, words, and deeds.
- Mahatma Gandhi applied this principle to his philosophy of non-violent resistance, inspiring global movements for social justice. Gandhi’s belief in ahimsa illustrates a universal respect for humanity, as he stated, “The best way to find yourself is to lose yourself in the service of others.”
1.6.2 – How liberty is understood in Indigenous beliefs
1.6.2.1 – Stewardship and liberty in Native American beliefs
- Many Native American tribes view humanity as an interconnected relationship between people, animals, and nature. This kinship includes respect for all living things and the belief that individuals are caretakers of the Earth. The Lakota phrase Mitákuye Oyás’iŋ (“we are all related”) embodies this holistic view of humanity.
- These values remind us of the importance of community and environmental stewardship, emphasizing humanity’s responsibility to respect not only other people but also the natural world.
1.6.2.2 – How liberty fosters unity in African traditions of Ubuntu
- Ubuntu, a Southern African philosophy, means “I am because we are.” It emphasizes community, shared humanity, and mutual support, highlighting that individuals thrive through connection and mutual respect.
- Nelson Mandela advocated for Ubuntu, saying, “A person with Ubuntu is open and available to others, affirming of others, and does not feel threatened that others are able and good.” This concept forms the foundation for social justice and equality, promoting the idea that humanity is strongest in unity.
1.6.3 – How liberty shapes secular views on humanity
1.6.3.1 – How humanism champions liberty and human rights
- Humanism, a secular ethical approach, celebrates the dignity, worth, and potential of the individual. It encourages reason, compassion, and respect for human rights, aiming to build a society based on mutual respect.
- Humanism promotes tolerance and empathy, asserting that humanity’s progress depends on collaboration and respect for all.
1.6.3.2 – How Confucianism relates liberty to social harmony
- In Confucianism, ren represents benevolence, encouraging individuals to treat others with respect, fairness, and kindness. Confucian teachings focus on family and societal harmony, emphasizing that treating others well creates a harmonious society.
- Confucius famously said, “What you do not wish for yourself, do not do to others.” This timeless principle guides ethical conduct and the practice of humanity.
1.6.4 – Liberty and universal values across cultures
Despite cultural and religious diversity, certain values are universally shared: empathy, kindness, justice, and a sense of community. These values highlight the importance of respecting individual dignity and acting to promote collective well-being. Humanity, expressed differently across traditions, encourages us to support one another, foster inclusivity, and uphold ethical principles that benefit society.
1.6.4.1 – How liberty fosters empathy and compassion in societies
- Humanity involves empathy and understanding others’ experiences. Compassion-driven ethics encourage mindfulness of others’ struggles and offer support whenever possible.
1.6.4.2 – Liberty, justice, and fairness in philosophical traditions
- Justice symbolizes equality and fairness, whether through religious commandments, cultural practices, or modern laws. The desire for fair treatment reflects humanity’s commitment to equity and moral balance.
1.6.4.3 – How liberty nurtures community responsibility across traditions
- Humanity includes a responsibility to contribute positively to one’s community and environment. Many philosophies emphasize communal support, stressing that collective strength fosters security and well-being.
1.6.5 – Top quotes on the global idea of humanity
1.6.5.1 – Compassionate happiness quote by Dalai Lama
“If you want others to be happy, practice compassion. If you want to be happy, practice compassion.” – Dalai Lama
1.6.5.2 – Quotes by Mahatma Gandhi on peaceful change
“Gently, you can shake the world.” – Mahatma Gandhi
1.6.5.3 – Justice over the absence of Tension quote by MLK
“True peace is not merely the absence of tension; it is the presence of justice.” – Martin Luther King Jr.
1.6.5.4 – MLK’s quote about human interconnectedness and mutuality
“We are caught in an inescapable network of mutuality, tied in a single garment of destiny.” – Martin Luther King Jr.
1.6.5.5 – John Donne’s quote on human interdependence
“No man is an island, entire of itself; every man is a piece of the continent, a part of the main.” – John Donne
1.7 – Global challenges to liberty in the modern world
Explore the global challenges threatening liberty today, from censorship to authoritarianism, and how they impact freedom in the modern world.
The modern world, while marked by scientific and technological advances, faces unprecedented challenges that impact humanity’s progress and survival. Issues like climate change, inequality, technological ethics, and geopolitical tensions are central to shaping future generations. These challenges, though contemporary, often have historical roots that set the stage for today’s struggles.
1.7.1 – Introduction to Modern Challenges to Humanity
In today’s interconnected world, humanity faces challenges that threaten both our survival and the quality of life. Climate change, social inequality, and technological ethics dominate current discussions, influencing both domestic and global landscapes. Understanding these issues requires looking at their historical foundations and considering their far-reaching effects.
1.7.2 – Section 1: How liberty influences climate change solutions and challenges
Climate change remains one of the most pressing threats to humanity. Rising global temperatures, melting ice caps, and natural disasters pose severe risks to ecosystems and human life. As a major contributor to global emissions, the U.S. plays a key role in addressing this crisis.
1.7.2.1 – Lessons on liberty and environmental care from Native American wisdom
“We do not inherit the earth from our ancestors; we borrow it from our children.” – Native American Proverb
Technological solutions, renewable energy, and individual responsibility are critical to mitigating climate impacts. Many are seeking practical ways to reduce their environmental footprint, making this an essential area of focus.
1.7.3 – Section 2: How liberty plays a role in reducing social inequality
Economic disparities and social inequality continue to fuel social unrest. In the U.S., income inequality, housing costs, healthcare expenses, and education fees strain middle- and lower-income families.
1.7.3.1 – The link between liberty, poverty, and social justice through Jane Addams’ reforms
Early 20th-century reformers like Jane Addams addressed urban poverty and championed workers’ rights, influencing modern labor movements and social programs.
By looking at the history of social welfare and civil rights movements, we can understand the progress made and the challenges that remain.
1.7.4 – Section 3: How liberty is essential in managing technological privacy challenges
The rise of the internet and artificial intelligence brings a new set of ethical challenges. In the U.S., where tech giants like Google, Apple, and Facebook dominate, concerns about data privacy, misinformation, and AI ethics are significant.
1.7.4.1 – Christian Lous Lange’s warning on liberty and technology
"Technology is a useful servant but a dangerous master." – Christian Lous Lange
This section highlights issues such as AI regulation, digital privacy laws, and cybersecurity. As concerns grow, providing insights into personal data protection and combating misinformation can resonate with readers.
1.7.5 – Section 4: Mental health, liberty, and social connection in a disconnected world
Despite technological advances, an unprecedented mental health crisis persists. Many report feelings of isolation and anxiety, worsened by the COVID-19 pandemic, social media pressures, and the fast-paced modern lifestyle.
1.7.5.1 – How liberty-driven community support is reshaping mental healthcare
During the Great Depression, community support played a key role in resilience, a spirit echoed today in online mental health initiatives.
Emphasizing mental health awareness, accessible therapy, and community support is essential. Providing relevant U.S.-based resources can be invaluable to readers seeking help.
1.7.6 – Section 5: Liberty, geopolitical tensions, and the pursuit of global peace
Humanity faces rising geopolitical tensions, with conflicts over resources, territories, and ideologies. As a leading global power, the U.S. often finds itself at the heart of these struggles, from trade disputes to diplomatic conflicts.
1.7.6.1 – Albert Einstein’s call for liberty and understanding in global peace
“Peace cannot be kept by force; it can only be achieved by understanding.” – Albert Einstein
This section discusses international policies, the role of global organizations like the United Nations, and the importance of treaties in maintaining peace and stability. Understanding these issues helps readers grasp the global forces shaping their lives.
1.7.7 – How Humanity Drives Technological Innovation with Liberty
Meta Description: “The Role of Humanity in Technology and Innovation”—exploring humanity’s influence on tech development and ethical progress in the modern age.
1.7.7.1 – How Liberty and Humanity Interact in Technological Progress
The intersection of humanity and technology is a defining feature of today’s world. As new advancements emerge, human values, ethics, and creativity shape technological progress. From pioneering entrepreneurs to everyday users, people’s engagement with technology reflects broader societal, ethical, and intellectual aspirations.
This article explores humanity’s contributions to technology and innovation, focusing on how these interactions mirror larger societal trends.
1.7.7.2 – Section 1: How Liberty and Human Values Inspire Technological Innovation
Groundbreaking technologies are rooted in values like progress, curiosity, and solving human problems. The American focus on individualism, freedom, and ingenuity has fueled transformative developments, from the internet to space exploration.
1.7.7.3 – Daniel Bell on Liberty and Human Imagination in Technology
“Technology, like art, is a soaring exercise of the human imagination.” – Daniel Bell, sociologist
This section highlights how foundational values drive technological growth, leading to innovations with global impact.
1.7.8 – Section 2: How Liberty Influences Ethical Standards in Technological Innovation
With rapid technological advancements, ethical considerations are crucial. From artificial intelligence to biotechnology, innovations must respect human rights and ethical standards. Ethical concerns are central to the technology shaping politics, privacy, and public discourse.
1.7.8.1 – The 1970s Data Privacy Debate
In the 1970s, the rise of computing technology sparked the first debates on data privacy, leading to landmark privacy laws that influence today’s standards.
This section discusses the role of ethical frameworks in technology, using examples like data privacy laws, AI regulations, and genetic modification debates.
1.7.9 – Section 3: How Liberty Shapes User Experience and Tech Development
Innovation is not just about functionality but also how it meets people’s needs. Human-centered design is a core principle in tech development, particularly with major companies like Apple and Google prioritizing user experience.
1.7.9.1 – Steve Jobs on Liberty in User Experience and Design
“Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.” – Steve Jobs
This section explores how user experience influences tech design, highlighting examples like smartphone interfaces and accessible online services.
1.7.10 – Section 4: How Liberty Fuels Collaboration in Technological Progress
Technological advancements often result from collaborative efforts, blending diverse talents and perspectives. In places like Silicon Valley, interdisciplinary teams and international talent drive progress, creating world-changing products.
1.7.10.1 – The Role of Liberty in Collaborative Tech Development
During the creation of the first personal computers, engineers, designers, and marketers worked closely to bring the concept to mainstream audiences, revolutionizing the tech landscape.
This section illustrates how teamwork and shared ideas drive innovation, with examples like smartphones, software, and space exploration.
1.7.11 – Section 5: How Liberty and Tech Can Shape a Better Future for Humanity
As humanity confronts challenges like climate change, resource scarcity, and social inequality, technology offers solutions. Emerging fields like sustainable tech, green energy, and medtech hold promise for addressing these issues and shaping a better future.
1.7.11.1 – Alan Kay on Liberty and Innovation Shaping the Future
“The best way to predict the future is to invent it.” – Alan Kay, computer scientist
1.8 – How humanity shapes the future through technology and social progress
Discover how humanity drives the future through technology and social progress, shaping liberty with innovation, equality, and transformative change.
1.8.1 – Overview of humanity’s role in shaping the future of technology and society
In a world of rapid technological and social change, humanity’s role in shaping the future has never been more critical. From breakthroughs in medicine and artificial intelligence to movements for social and environmental justice, today’s choices lay the groundwork for tomorrow. This article examines how human actions and values influence future directions, focusing on key global dynamics.
1.8.2 – Section 1: How human values shape groundbreaking technological innovations
Human values such as empathy, curiosity, and resilience are fundamental drivers behind advancements in technology, healthcare, and education. In places where technological and scientific research thrives, these values help shape innovations with both local and global impact.
1.8.2.1 – Franklin D. Roosevelt’s quote on the role of doubt in shaping the future
“The only limit to our realization of tomorrow will be our doubts of today.” – Franklin D. Roosevelt
This section highlights how core human values are embedded in the pursuit of progress, from compassionate healthcare solutions to groundbreaking space exploration. These innovations are shaped by ethical considerations, prioritizing human impact.
1.8.3 – Section 2: How education drives the future of technology and scientific innovation
Education is central to empowering individuals and developing future leaders, scientists, and thinkers. Particularly in STEM fields, education shapes the future by influencing technological and scientific advancements.
1.8.3.1 – How Sputnik’s launch transformed U.S. focus on science education
After the Sputnik launch, there was a renewed emphasis on science education in the U.S., leading to significant advancements in space technology that continue to shape the future.
This section underscores the transformative power of education in fostering critical thinking and innovation. The importance of learning extends beyond individual achievement, contributing to societal progress.
1.8.4 – Section 3: How humanity plays a key role in preserving the environment
As environmental challenges intensify, humanity’s responsibility to conserve resources and develop sustainable solutions grows. This section explores the critical role individuals and communities play in addressing climate change, reducing carbon emissions, supporting green energy, and preserving biodiversity.
1.8.4.1 – Environmental sustainability lessons from Chief Seattle’s quote
“The earth does not belong to us: we belong to the earth.” – Chief Seattle
The growing interest in sustainability highlights how collective and individual actions contribute to a greener future. Practical insights on how to integrate sustainability into everyday life are key to moving forward.
1.8.5 – Section 4: Humanity’s fight for equality through social justice movements
Social justice movements represent humanity’s ongoing fight for equality, fairness, and human rights. These movements have sparked significant changes, from civil rights to gender equality, influencing the global future.
1.8.5.1 – How the Civil Rights Movement reshaped equality movements worldwide
The U.S. civil rights movement of the 1960s transformed societal norms, inspiring future generations to oppose oppression and inequality.
This section examines the evolution of social movements, addressing issues such as racial equality, LGBTQ+ rights, and gender equity. The ongoing pursuit of justice continues to shape a more equitable society.
1.8.6 – Section 5: How humanity must guide the future of technology integration
As technology becomes increasingly integrated into everyday life, humanity’s role in directing these advancements grows. Emerging fields like artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and digital ethics demand ethical oversight and consideration.
1.8.6.1 – Albert Einstein’s wisdom on human spirit and technology
“The human spirit must prevail over technology.” – Albert Einstein
This section explores how technologies, especially AI and genetic modification, should be developed with ethical boundaries in mind. As technology shapes the future, the balance between innovation and responsibility is crucial.
1.9 – Liberty and Its Historical Significance in Modern Society
Discover the historical impact of liberty on modern society, exploring its evolution, key milestones, and lasting influence on democracy and individual freedoms.
Humanity’s role in shaping the future is interconnected with our values, actions, and innovations. From technological and educational advancements to social justice and environmental sustainability, our choices today will influence what lies ahead. By fostering compassion, curiosity, and responsibility, we can create meaningful change. Staying informed empowers everyone to contribute to a better world, as collective efforts lead to global progress. Our shared dedication to ethical decision-making and unity of purpose will shape a better future for generations to come.